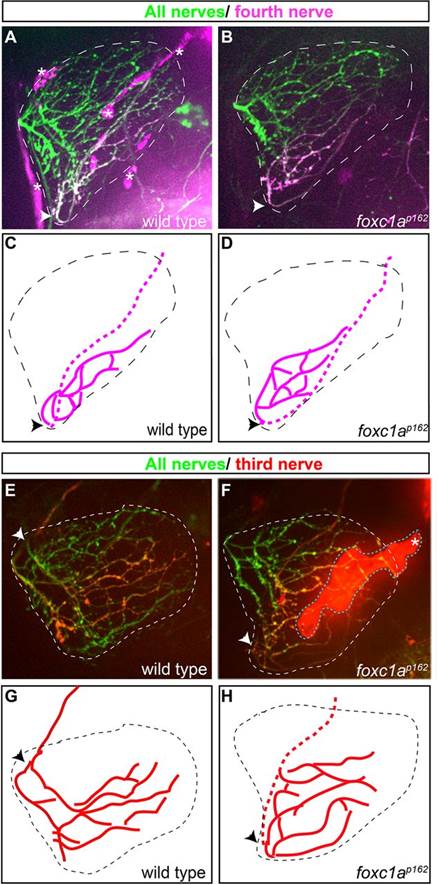
Fig. 5
Motor axons select their synaptic target independently of their migration history. (A-D) In wild type and foxc1a mutants, photoconverted Kik-GR-positive axons of the fourth fin nerve enter the fin at the ventral point of the fin and project to their ventroposterior target area. Arrowheads indicate where the nerve enters the fin. (E-H) In foxc1a mutants, photoconverted Kik-GR-positive axons of the third fin nerve enter the fin at an ectopic, ventral point of the fin yet project to the same target area as the corresponding wild-type axons that entered through the endogenous dorsal fin entry point. Red and magenta lines show tracing of photoconverted third and fourth nerves, respectively. Dotted lengths of red and magenta lines denote regions of the nerve underneath the fin. Asterisks (in A and F) and cyan dashed area (F) mark non-neural tissues giving background fluorescence in red channel. Scale bar: 50Ám.