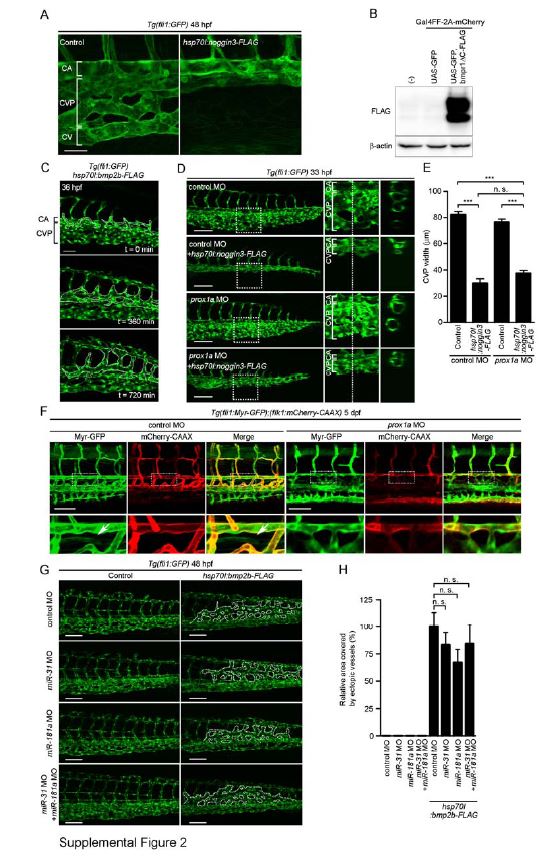
Fig. S2 Bmp Regulates CVP Formation. Related to Figure 2. (A) Confocal z-stack images of the caudal regions of 48 hpf Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos injected without (Control) or with hsp70l:noggin3-FLAG Tol2 plasmid and heat-shocked at 22 hpf for 2 h. Note that overexpression of Noggin3-FLAG, a Bmp antagonist, inhibited formation of CV and CVP, but did not affect CA formation. (B) 293T cells were transfected without (-) or with Gal4-driven expression vector encoding GFP (UAS:GFP) or that encoding both GFP and Bmpr1?C-FLAG (UAS:GFP,bmpr1?C) together with the plasmid encoding Gal4FF-2A-mCherry, and subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-FLAG and anti-β-actin antibodies. A UAS:GFP,bmpr1?C plasmid can drive expression of GFP and Bmpr1?C-FLAG simultaneously in a Gal4-dependent manner. (C) Confocal z-stack images of the caudal regions of 36 hpf Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos injected with hsp70l:bmp2b-FLAG Tol2 plasmid and heat-shocked at 24 hpf for 30 min and its subsequent time-lapse images at the indicated time point. Dotted lines indicate ectopic venous vessels. Note that overexpression of Bmp2b resulted in formation of ectopic vessels sprouted from the CVP. (D) Projection view of confocal z-stack images on the caudal region of 33 hpf Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos injected with 5 ng control MO or 5 ng prox1a MO together without or with hsp70l:noggin3-FLAG Tol2 plasmid are shown, as in Figure 1G. (E) The width of CVP as observed in D was quantified, as in Figure 1H (control MO [n=8], control MO + hsp70l:noggin3-FLAG [n=9], prox1a MO [n=9], prox1a MO + hsp70l:noggin3-FLAG [n=8]). (F) 3D-rendered confocal images of the trunk regions of 5 day postfertilization (dpf) Tg(fli1:Myr-GFP);(flk1:mCherry-CAAX) embryos injected with 5 ng control MO or 5 ng prox1a MO. GFP (Myr-GFP), mCherry (mCherry-CAAX) and the merged images (GFP, green; mCherry, red) are shown as indicated at the top. The boxed areas are enlarged on the panels beneath the original images. Arrows indicate thoracic duct. Note that prox1a morphant exhibited defective formation of thoracic duct. (G) Projection view of confocal z-stack images of the caudal regions of 48 hpf Tg(fli1:GFP) embryos injected with 5 ng control MO (control MO), 5 ng miR-31 MO (miR-31 MO), 5 ng miR-181a MO (miR-181a MO) or a mixture of 5 ng miR-31 MO and 5 ng miR-181a MO (miR-31 MO + miR-181a MO) together without (Control) or with hsp70l:bmp2b-FLAG Tol2 (hsp70l:bmp2b-FLAG) plasmid, and heat-shocked at 24 hpf for 30 min. Dotted lines indicate ectopic venous vessels. Note that knockdown of miR-31 and/or miR-181a did not affect Bmp2b-induced formation of ectopic venous vessels. (H) The area covered by ectopic venous vessels as observed in G was quantified and expressed as percentages relative to that observed in the embryos injected with both control MO and hsp70l:bmp2b-FLAG-Tol2 plasmid. Data are shown as mean ▒ s.e.m. (n=3). Scale bars, 50 Ám (A and F) and 100 Ám (D and G). ***p<0.001. n.s., no significance.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 32, Wakayama, Y., Fukuhara, S., Ando, K., Matsuda, M., Mochizuki, N., Cdc42 Mediates Bmp-Induced Sprouting Angiogenesis through Fmnl3-Driven Assembly of Endothelial Filopodia in Zebrafish, 109-22, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell