Fig. 4
Fig. 4
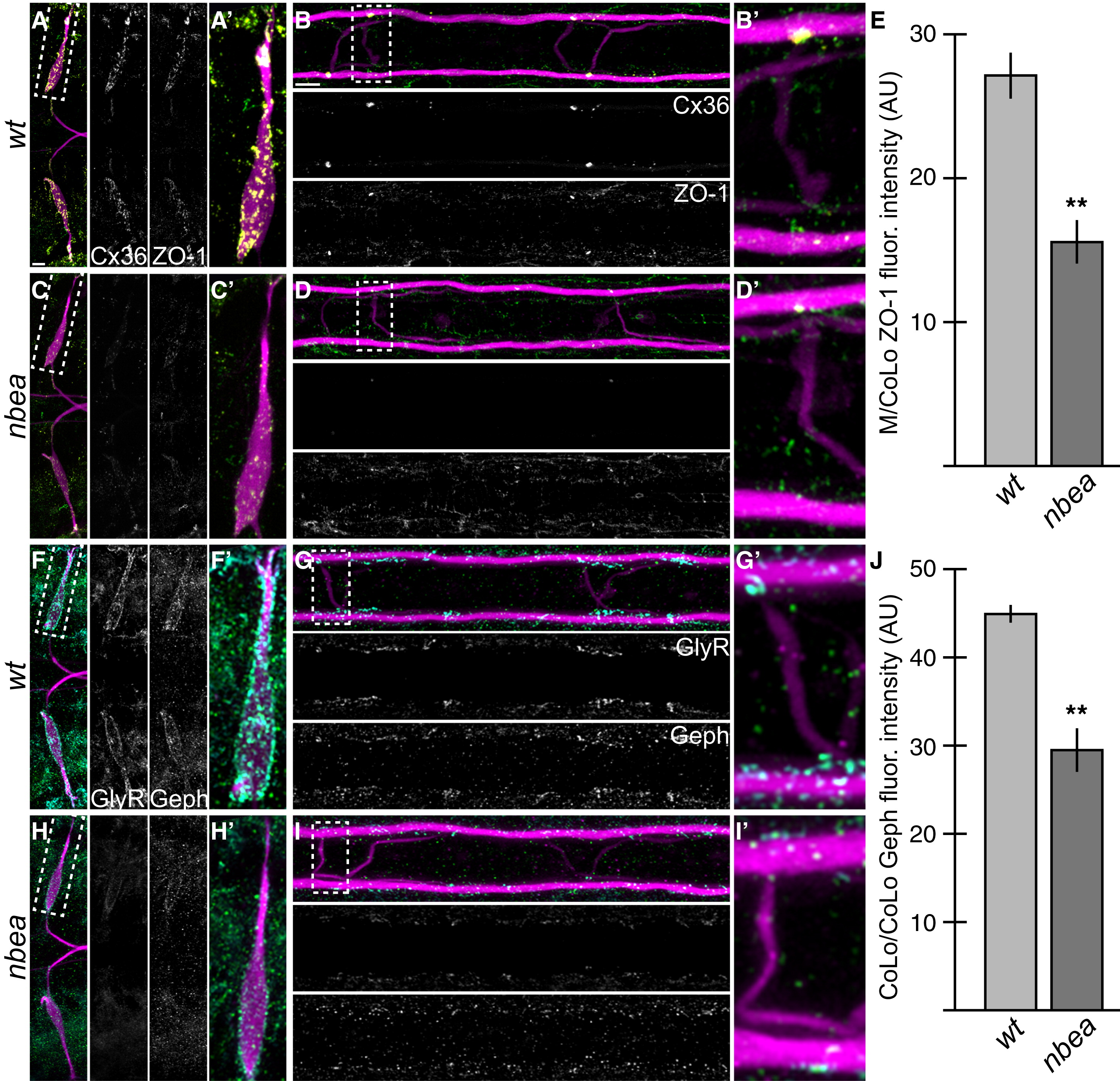
Electrical and Chemical Synaptic Scaffolds Are Disrupted in nbea Mutants
(A?D and F?I) Larvae are stained for GFP (magenta) in all panels, Cx36 (yellow) and ZO-1 (green) in (A)?(D), and GlyR (cyan) and Gephyrin (Geph, green) in (F)?(I). Individual Cx36, ZO-1, GlyR, and Geph channels are shown in neighboring panels. Note that for each spinal cord zoom, there is only one M/CoLo and CoLo/CoLo synapse depicted; this is due to natural variation in the positions of CoLo neurons in the spinal cord.
(A?D) The electrical synapse scaffold ZO-1 is colocalized with Cx36 at M dendritic (A and A′) and spinal cord (B and B′) synapses. ZO-1 staining is diminished in mutants (C and D), but less severely than Cx36.
(E) Quantitation of ZO-1 at M/CoLo synapses in wild-type and nbea mutants.
(F?I) The inhibitory synapse scaffold Geph is colocalized with GlyR at M dendritic (F and F′) and CoLo spinal cord (G and G′) synapses. Geph staining is diminished in mutants (H and I), but less severely than GlyR.
(J) Quantitation of Geph at CoLo/CoLo synapses in wild-type and nbea mutants.
Graphs in (E) and (J) represent data as mean ± SEM. p < 0.01 compared to control.
Associated experimental statistics are found in Table S2.