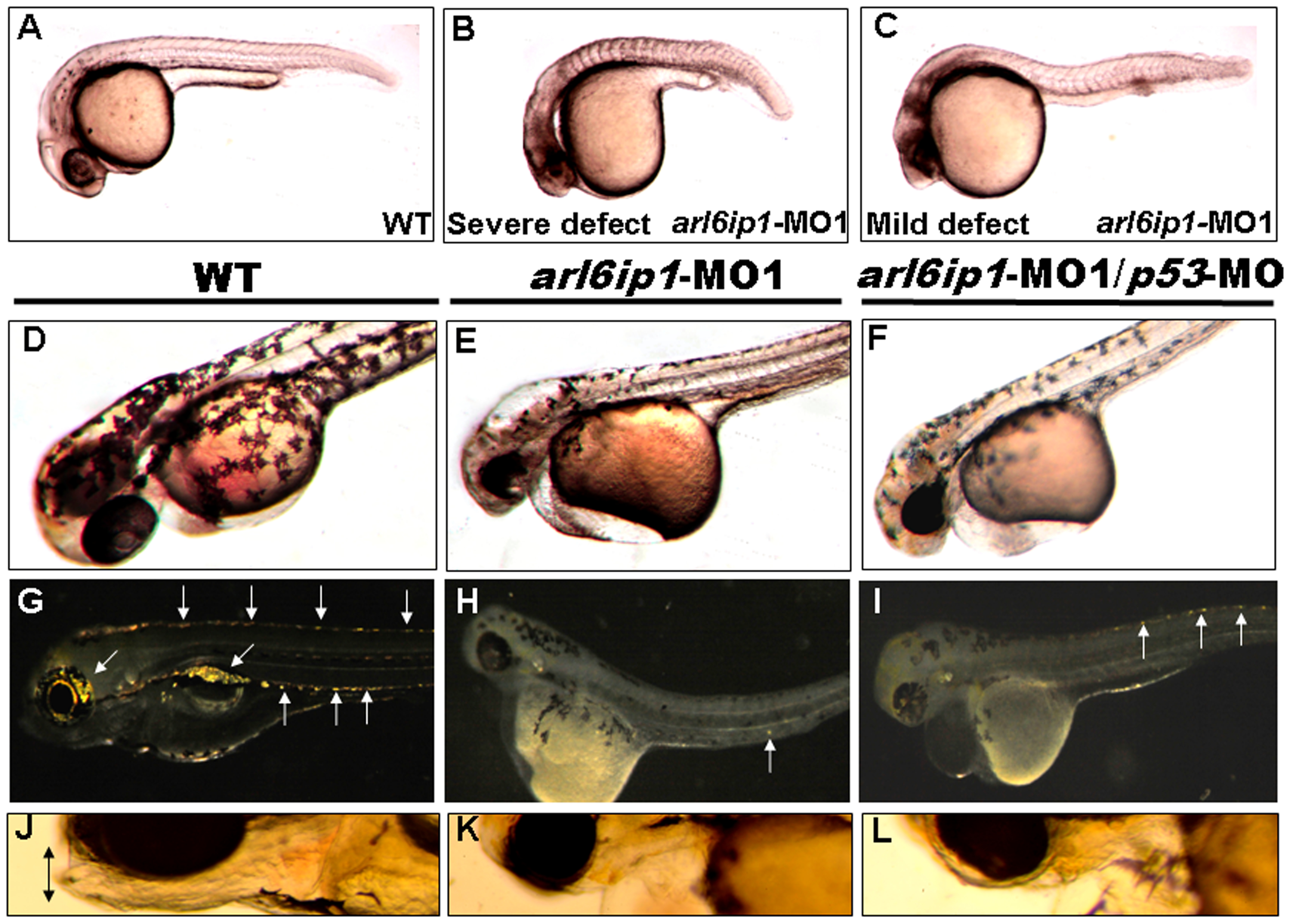
Fig. 1 Embryos injected with arl6ip1-MO1 display abnormal development in ectoderm-derived tissues.
Lateral views of embryos at 24 hpf (A-C), 48hpf (D-F) or at 96 hpf (G-L). (A) Wild-type (WT) embryos at 24 hpf displayed normal embryonic morphology. (B) Embryos injected with arl6ip1-MO1 exhibited foreshortened yolk extension and tail and small head with eye lesions. These embryos were defined as having severe defects. (C) Embryos with mild defects showed longer axis than embryos with severe defects. However, similar to embryos with severe defects, eye development was nearly equally compromised. (D) At 48hpf, WT embryos displayed plentiful melanophores. (E, F) Melanophores were highly reduced in arl6ip1-MO1 and arl6ip1-MO1/p53-MO-injected embryos. (G) Iridophores (arrows) were prominent in 4 dpf WT embryos. (H) Iridophores were almost absent in arl6ip1-MO1 embryos (only 1 residual cell was seen here in the ventral of the trunk) and (I) highly reduced in arl6ip1-MO1/p53-MO-injected embryos. (J) WT embryos showed well-developed head, jaw and melanophores. (K, L) arl6ip1-MO1 and arl6ip1-MO1/p53-MO-injected embryos displayed reduced head size and jaw (double arrows), but the head of arl6ip1-MO1/p53-MO embryos was bigger than arl6ip1 morphants.