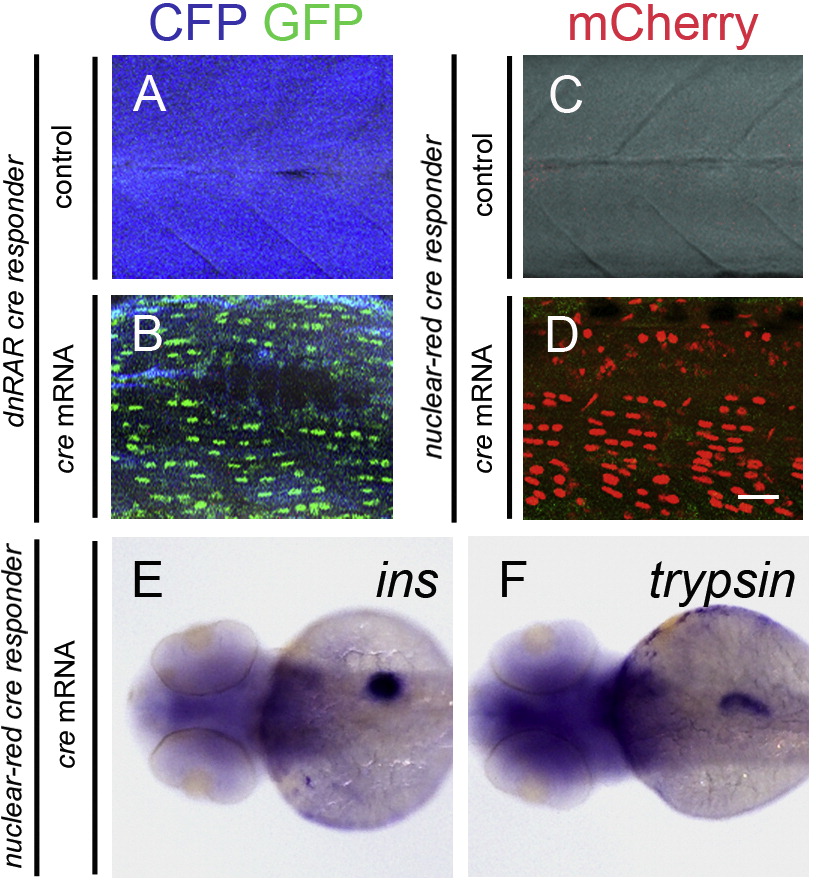
Fig. S6
Injection of cre mRNA induces expression of dnRAR in the larvae of dnRAR cre responder, but does not change the expression pattern of ins and trypsin in the larvae of nuclear-red cre responder. (A and B) Fluorescent images of the larval somites of dnRAR cre responder at 72 hpf. (A) Non-cre mRNA injected larvae (negative control). (B) cre mRNA injected larvae. cre mRNA was injected at one cell stage. Widespread expression of nuclear-GFP can be detected in the larvae with cre mRNA injection, but not in the control. (C and D) Fluorescent images of the larvae somites of nuclear-red cre responder at 72 hpf. (C) Non-cre mRNA injected larvae. (D) cre mRNA injected larvae. cre mRNA injection robustly induces the recombination of LoxP sites, indicted by the widespread expression of nuclear-mCherry, but not in the non-injected controls. Scale bar in A?D, 10 μm. (E and F) In situ hybridization images of the nuclear-red cre responder larvae at 72 hpf. Cre mRNA was injected into the embryos at one-cell stage. (E) ins expression in the larvae. (F) trypsin expression in the larvae. Injection of cre and subsequent recombination does not affect pancreatic development.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 394(1), Huang, W., Wang, G., Delaspre, F., Vitery, M.D., Beer, R.L., Parsons, M.J., Retinoic acid plays an evolutionarily conserved and biphasic role in pancreas development, 83-93, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.