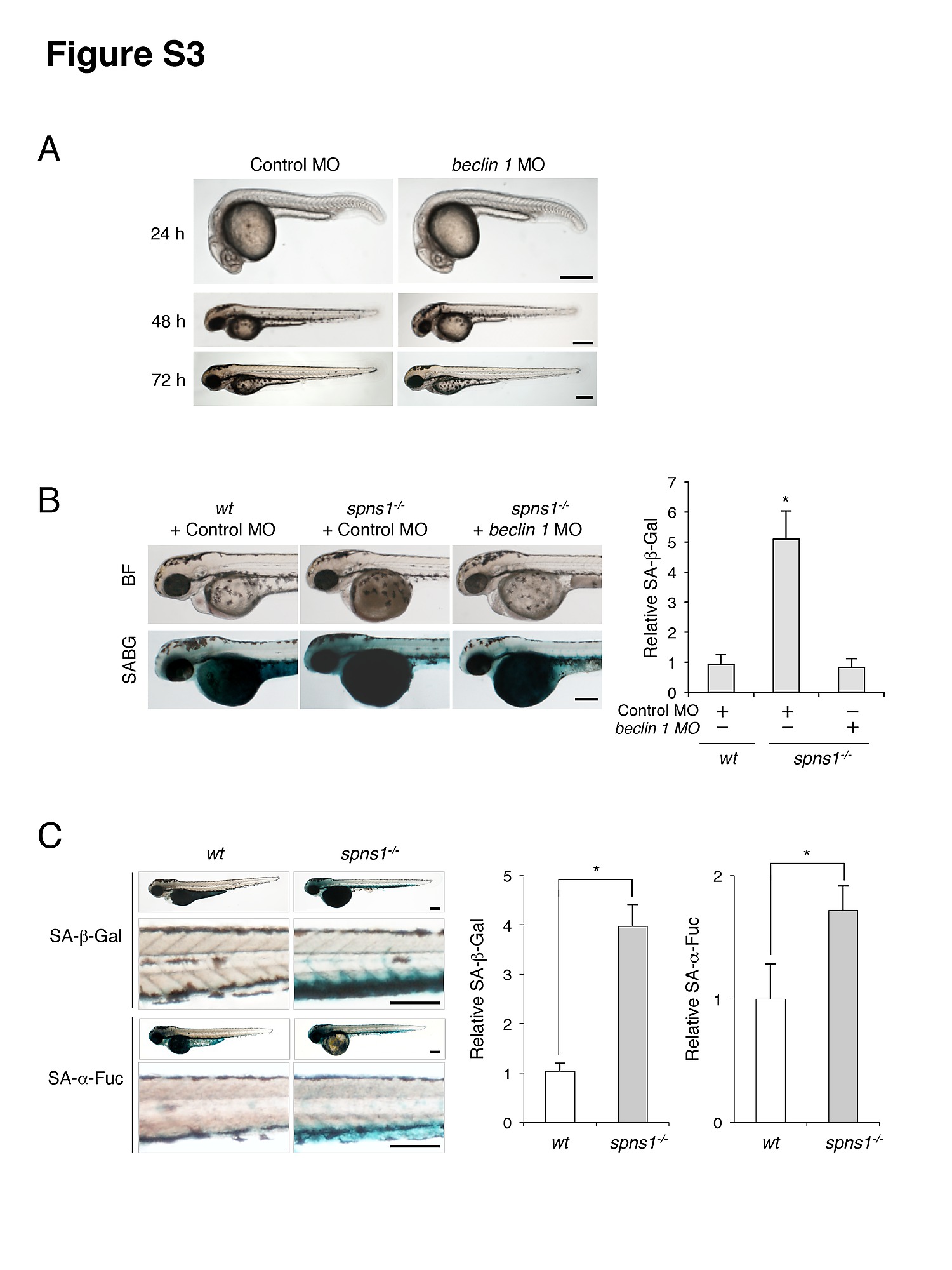
Fig. S3
Impact of Beclin 1 depletion on the yolk opaque phenotype and embryonic senescence in spns1-mutant zebrafish. (A) Phenotype of beclin 1 morphant (beclin 1 MO, 12 ng/embryo) at 24, 48 and 72 hpf. Scale bar, 250 μm. (B) Effect of beclin 1 knockdown in the spns1 mutant on the phenotypes of yolk opacity (BF; bright field) and on embryonic senescence (SABG; SA-β-gal) in the spns1 mutant. Following injection of standard control MO or beclin 1 MO (12 ng/embryo) into Tg(CMV:EGFP-LC3); spns1hi891/hi891 embryos, SA-β-gal staining was performed to determine whether the beclin 1 knockdown had any impact on embryonic senescence caused by Spns1 depletion at 84 hpf. Scale bar, 250 μm. Quantification of data presented in panel B (n = 12) is shown in the right graph; the number (n) of animals is for each morphant. (C) Parallel analyses of SA-β-gal and SA-α-fuc demonstrate the significant inductions of both activities in spns1-mutant animals at 84 hpf. As shown in the magnified panels, the caudal venous plexus (CVP) was the most prominently stained region. Staining for SA-β-gal was more intensive than for SA-α-fuc. Scale bar, 250 μm. Quantification of data presented in panel C (n = 12) is shown in the right graph; the number (n) of animals is for each morphant. Error bars represent the mean ± S.D., *p<0.005.