Fig. 3
Fig. 3
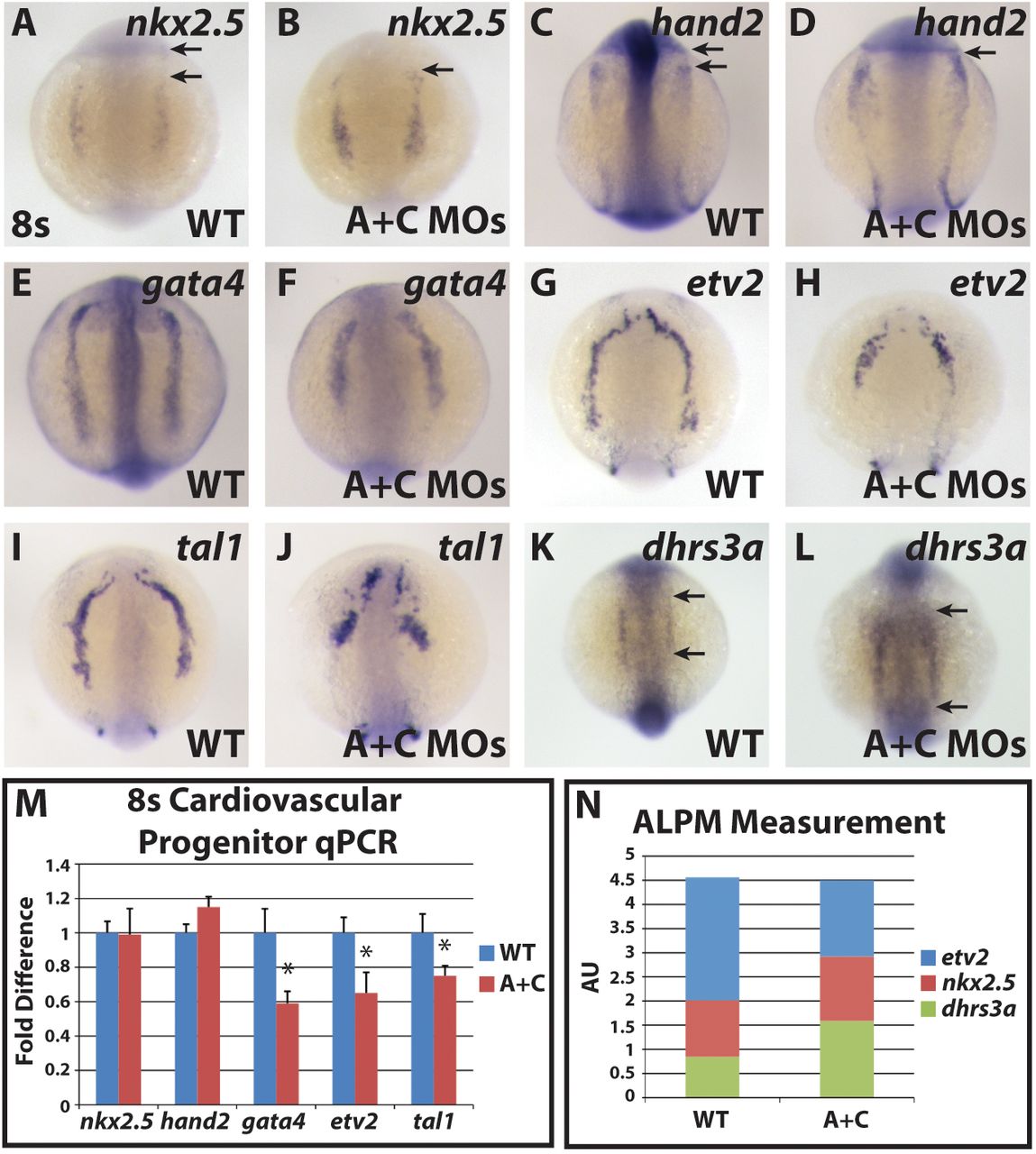
ALPM progenitor markers are shifted anteriorly in Cyp26-deficient embryos. In situ hybridization of (A,B) nkx2.5, (C,D) hand2, (E,F) gata4, (G,H) etv2, (I,J) tal1 and (K,L) dhrs3a in wild-type and Cyp26-deficient embryos. (A-D) There is an anterior shift in nkx2.5 and hand2 expression in Cyp26-deficient embryos. Arrows in A and C indicates distances between expression and posterior eye. Arrows in B and D indicate border between expression and posterior eye, which abut in Cyp26-deficient embryos. (E-J) gata4, etv2 and tal1 expression is truncated in Cyp26-deficient embryos compared with wild-type siblings. (K,L) dhrs3a expression is expanded in Cyp26-deficient embryos. Arrows indicate length of expression. The posterior boundaries of dhrs3a expression did not overtly change in control sibling and Cyp26-deficient embryos. (M) RT-qPCR of cardiovascular progenitor genes. Cyp26-deficient embryos have decreased gata4, etv2 and tal1 expression compared with wild-type siblings. (N) Total ALPM length is the same in wild-type and Cyp26-deficient embryos. For WT: n=22 (etv2), n=10 (nkx2.5), n=21 (dhrs3a). For Cyp26-deficient: n=17 (etv2), n=12 (nkx2.5), n=20 (dhrs3a). All images are dorsal views with anterior upwards. Significant differences compared with controls are indicated (*P<0.05). Error bars indicate s.d.