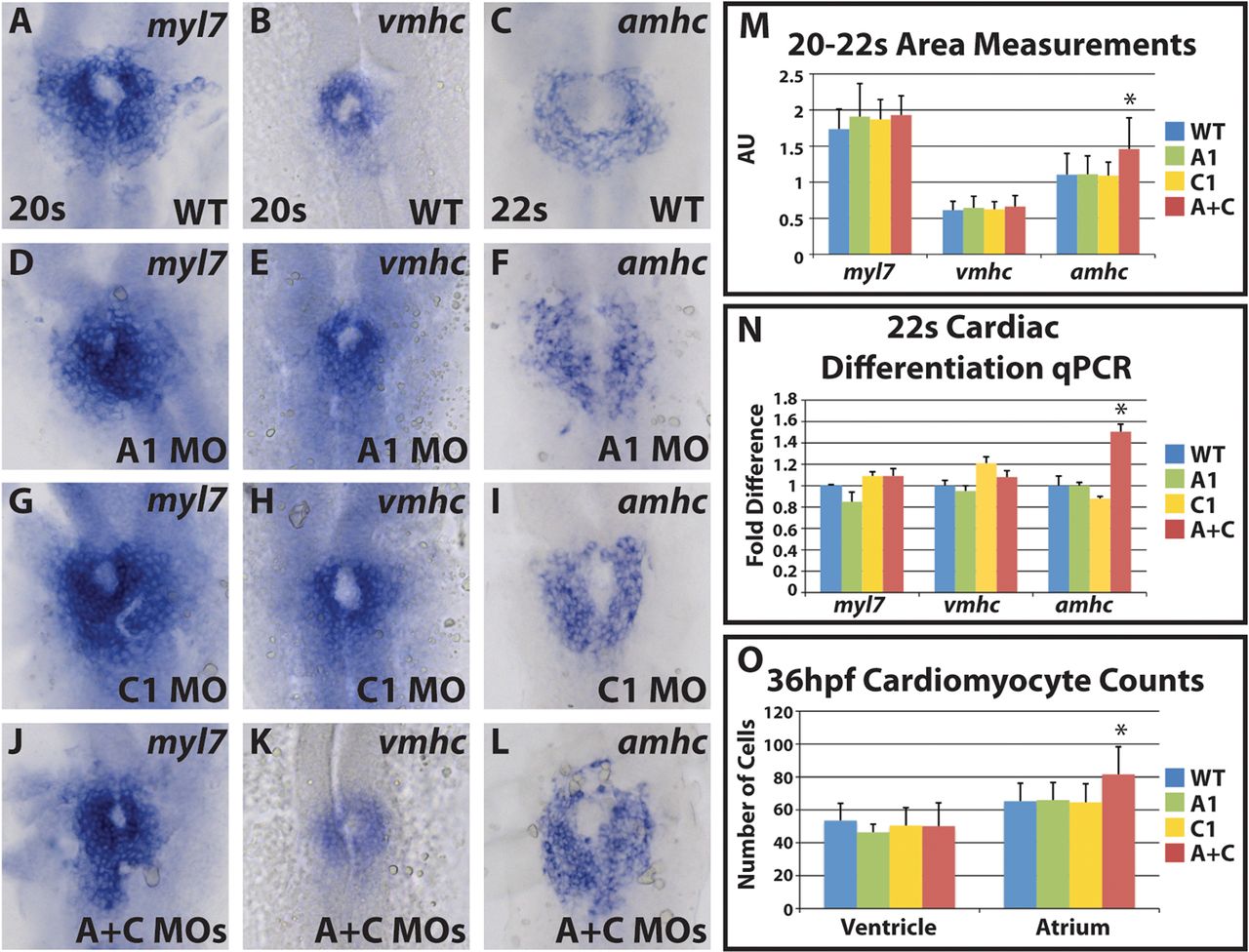
Fig. 2
Cyp26-deficient embryos have increased atrial differentiation and cell number. (A-L) Cardiac differentiation marker expression in wild-type, cyp26a1-deficient, cyp26c1-deficient and cyp26-deficient embryos. Singular knock down of cyp26a1 (D-F) or cyp26c1 (G-I) does not affect cardiac differentiation. Double knockdown (J-L) shows an expansion of amhc expression. (M) Area measurements indicate that amhc expression is expanded in Cyp26-deficient embryos. For myl7: WT, n=38; Cyp26a1-deficient, n=12; Cyp26c1-deficient, n=18; Cyp26-deficient, n=30. For vmhc: WT, n=40; Cyp26a1-deficient, n=19; Cyp26c1-deficient, n=16; Cyp26-deficient, n=37. For amhc: WT, n=33; Cyp26a1-deficient, n=17; Cyp26c1-deficient, n=17; Cyp26-deficient, n=41. (N) RT-qPCR indicates that only amhc expression is increased in Cyp26-deficient embryos. (O) Cardiomyocyte counts reveal a specific increase in atrial cells in Cyp26-deficient embryos at 36hpf. WT, n=53; Cyp26a1-deficient, n=15; Cyp26c1-deficient, n=15; Cyp26 deficient, n=51. All images are dorsal views with anterior upwards. Significant differences compared with controls are indicated (*P<0.05). Error bars indicate s.d.