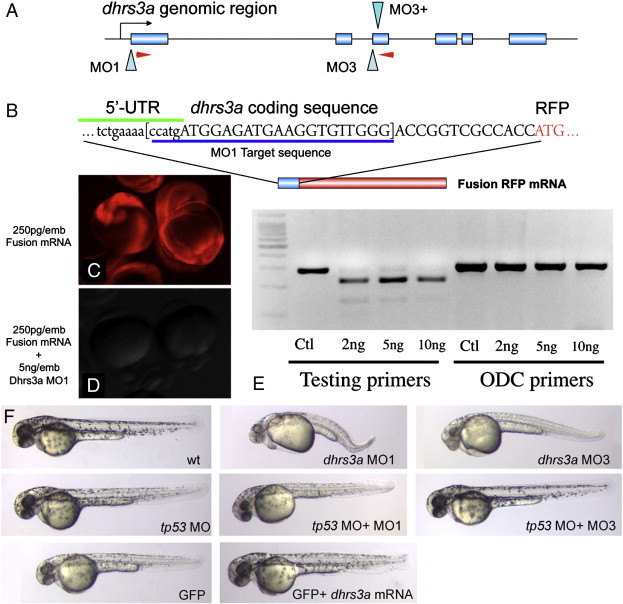
Fig. S1 Dhrs3a morpholinos effectively knock down gene function. (A) genomic structure of the zebrafish dhrs3a locus. Two sets of morpholinos were designed. MO1 blocks translation, while MO3 and MO3+ together block splicing of exon 2 by blocking the canonical splice site and an internal, cryptic splice site within intron 3. Red arrowheads indicate primer positions for RT-PCR in (E). (B) The dhrs3a-RFP fusion mRNA used to test the efficacy of MO1. (C, D) Translation of 250 pg of this fusion mRNA can be blocked by MO1 when injected at 5 ng/embryo. (E) RT-PCR of mRNA isolated from 12 hpf embryos injected with increasing amounts of MO3 and MO3+. Lanes 1-4: amplification with dhrs3a primers shown in A; lanes 5-8: amplification with control primers for the ornithine decarboxylase locus. (F) shows 48-h MO or mRNA-injected embryos. Toxicity of dhrs3a MO1 and MO3 can be rescued by co-injection of tp53MO.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 338(1), Feng, L., Hernandez, R.E., Waxman, J.S., Yelon, D., and Moens, C.B., Dhrs3a regulates retinoic acid biosynthesis through a feedback inhibition mechanism, 1-14, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.