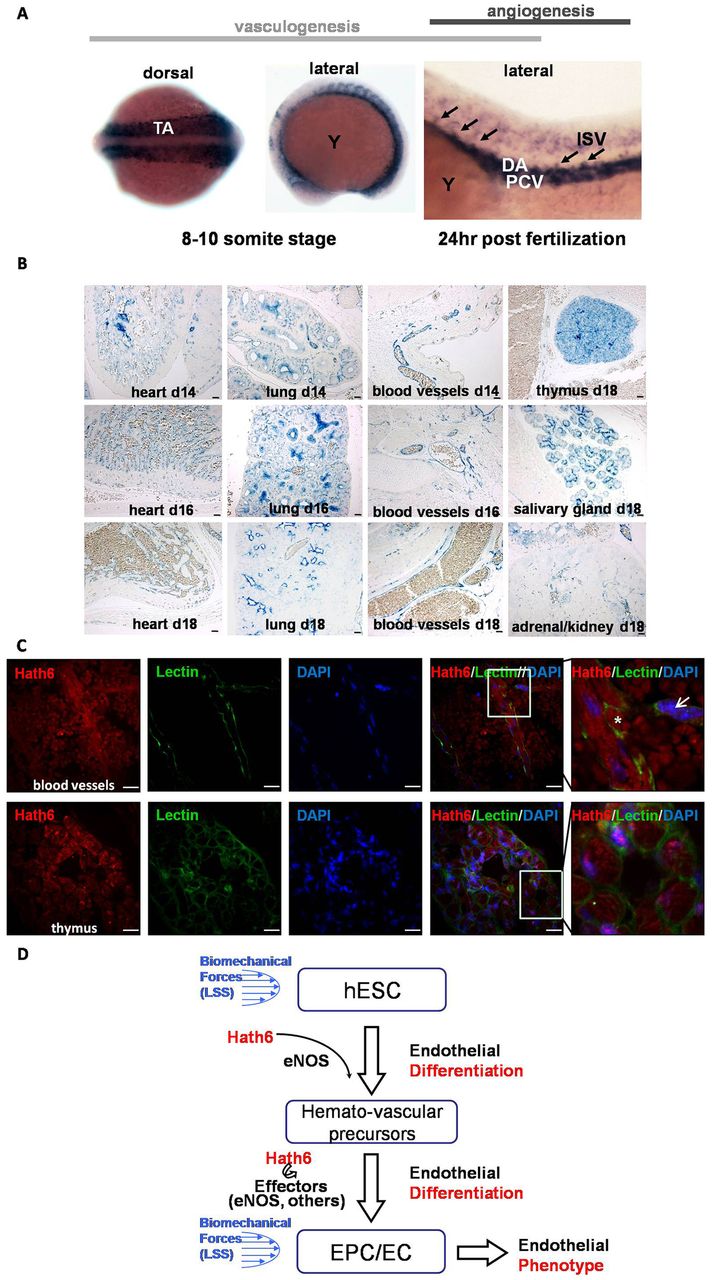
Fig. 7
Expression of Hath6 (Atoh8) in zebrafish and mouse embryos. (A) Whole-mount RNA in situ hybridization was performed on staged zebrafish embryos with an ath6 (zebrafish homolog of human Hath6) anti-sense riboprobe. A probe for ath6 was employed for in situ hybridization on embryos at the 8–10 somite stage (the left image shows the dorsal view and the middle image shows the lateral view) and 24hours post-fertilization (the right image, lateral view). A positive signal is shown as dark blue. Representative intersegmental arteries are denoted by black arrows. DA, dorsal aorta; ISV, intersegmental vessel; PCV, posterior cardinal vein; TA, trunk angioblasts; Y, yolk). (B) Expression of Math6, the murine homolog of Hath6, during embryonic development in vivo. In situ hybridization was performed on murine embryos at d14–18. An anti-sense digoxigenin-labeled riboprobe for Math6 was employed for in situ hybridization on sections of murine embryos. Tyramide-mediated signal amplification was used to detect probe hybridization. Sense control probes did not yield a signal (data not shown). Math6 was detected in the perivascular and blood-vessel wall; however, staining in non-endothelial tissues is also observed. Scale bars: 100 μm. (C) Confocal microscopy of sections from an E18 mouse embryo indicates the colocalization of Hath6 (red) with the endothelial marker fluorescein griffonia (bandeiraea) simplicifolia lectin II (GSLII, green). The upper panels show blood vessels with enucleated red blood cells (red autofluorescence without blue nuclear staining; indicated with an asterisk). The nuclear staining of Hath6 and the membrane staining with GSLII on the same cell is indicated with an arrow. The lower panels show images of the thymus. The white-boxed area is magnified in the right-most panel. Scale bars: 20μm. (D) A working model of Hath6 in endothelial differentiation and function. Treatment with biomechanical forces induces Hath6 mRNA expression in hESCs or endothelial cells, which results in increased differentiation of hemato-vascular precursors, endothelial progenitors and endothelial cells, and endothelial phenotype. eNOS is one of the mediators of Hath6 function.