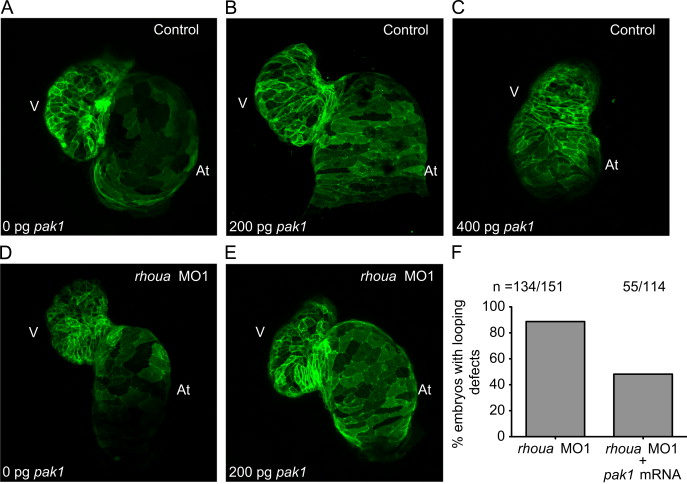
Fig. 6 Pak1 is able to rescue the rhoua MO injected zebrafish cardiac phenotype, but high dose Pak1 results in dysmorphic hearts. (A?C) Although injection of 200 pg of pak1 RNA into control MO Tg(cmlc2:ras-eGFP)s883 zebrafish embryos did not cause any significant cardiac phenotypes, injection of 400 pg of pak1 resulted in dysmorphic hearts. Tg(cmlc2:ras-eGFP)s883 (A) 0 pg pak1 RNA, (B) 200 pg pak1 RNA, and (C) 400 pg pak1 RNA injected into control MO embryos. (D, E) Injection of 200 pg of pak1 RNA was able to rescue the cardiac phenotype in the rhoua MO1 knockdown zebrafish. Tg(cmlc2:ras-eGFP)s883 (D) rhoua MO1 and (E) rhoua MO1+200 pg pak1 RNA injected embryos. (F) 88.7% of rhoua MO1 knockdown zebrafish embryos exhibited cardiac edema and AV canal defects, but injection of 200 pg of pak1 RNA reduced the cardiac phenotype to 48.2%. n indicates the number of embryos with cardiac phenotype/total number of embryos injected for each condition. At ? atrium, V ? ventricle.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 389, Dickover, M., Hegarty, J.M., Ly, K., Lopez, D., Yang, H., Zhang, R., Tedeschi, N., Hsiai, T.K., Chi, N.C., The atypical Rho GTPase, RhoU, regulates cell-adhesion molecules during cardiac morphogenesis, 182-91, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.