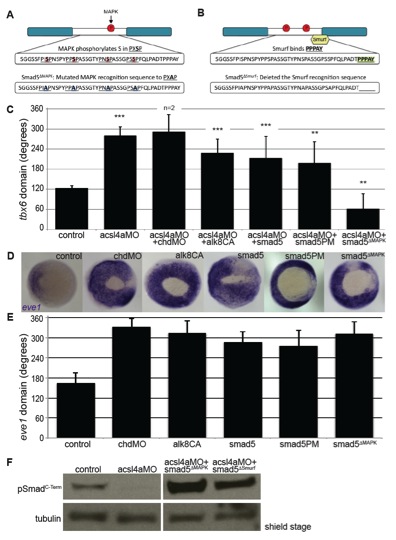
Fig. S5 Epistasis analysis of Bmp signaling cascade, related to Figure 4. (A-B) Diagrams of Smad5 constructs, showing mutated residues in the linker region. (A) MAPK-insensitive Smad5: Smad5ΔMAPK (B) Non-degradable Smad5: Smad5ΔSmurf (C) Quantification of the angle of tbx6 expression from whole-mount in situ hybridization after injection with acsl4a MO (750 fmol) alone or combined with chordin morpholino (chdMO 20fmol), constitutively active alk8 mRNA (alk8CA 1.5 ng) mRNA, C-terminal phosphomimic smad5 (smad5PM 1.5 ng) mRNA, and MAPK-insensitive smad5 (smad5ΔMAPK 1.5 ng) mRNA. Data are represented as mean of experimental means ± pooled SE. For acsl4a MO + chordin MO, data are represented as mean of experimental means ± pooled SD (n=2-8 experiments, 12-80 embryos/experiment). ANOVA with Dunnett post-hoc test was performed; acsl4a MO + chordin MO data was excluded from analysis. ** p d0.005, *** p<0.0001: compared to control. (D-E) Constructs used for rescue analysis in Figures 2B&C, 4B&C and S5A ventralize embryos to a similar extent. (D) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of ventral mesoderm marker eve1 after injection with chordin MO or mRNAs from Figures 2B&C, 4B&C and S5A. Injections were performed in parallel (i.e., with the same injection needle) with those in Figures 2B&C, 4B&C and S5A. Vegetal pole view, dorsal to the right (80% epiboly). (E) Data are represented as mean of experimental means ± pooled SD (n=2-7 experiments, 8-47 embryos/experiment). (F) Smad5 mutant constructs are phosphorylated by the Bmp receptor independent of Acsl4a. Representative western blot (n=4) of C-Terminal phosphorylated Smad (pSmadC-Term) from control embryos, embryos injected with acsl4a MO (750 fmol) or embryo injected with acsl4a MO combined with smad5ΔMAPK (1.5 ng) or smad5ΔSmurf (1.5 ng) mRNA. Anti-alpha tubulin is shown as a loading control. An extraneous lane between acsl4a MO and acsl4a MO + smad5ΔMAPK is omitted.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 27(6), Miyares, R.L., Stein, C., Renisch, B., Anderson, J.L., Hammerschmidt, M., and Farber, S.A., Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4A Regulates Smad Activity and Dorsoventral Patterning in the Zebrafish Embryo, 635-647, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell