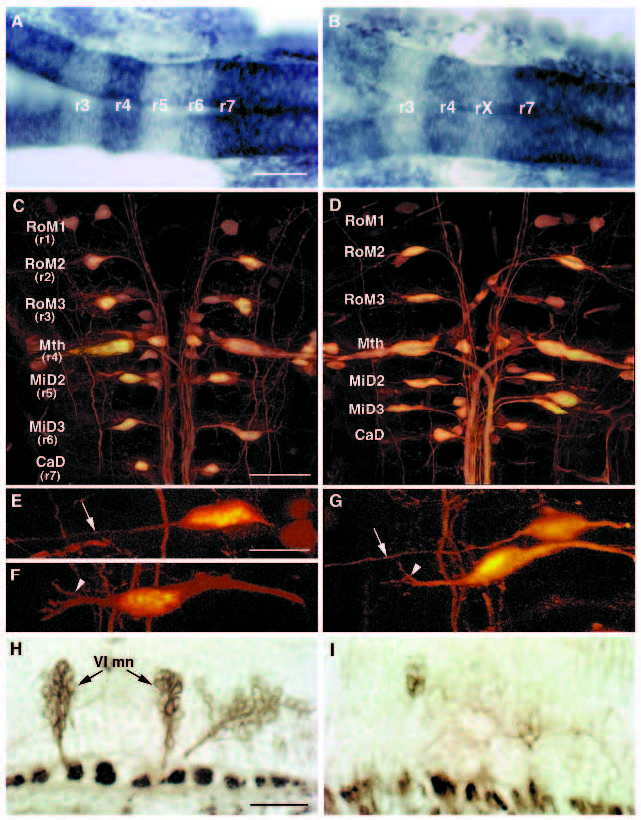
Fig. 3 The hindbrain of val- embryos is reduced by the length of one rhombomere. (A,B) Dorsal view of 22 h wild-type (A) and val- (B) embryos showing expression of two genes: g13.1 in r4 and anterior to the r2-r3 boundary and hdc posterior to the r6-r7 boundary. Anterior is to the left. The distance between the posterior boundary of g13.1 expression in r4 and the anterior boundary of hdc expression is reduced by the length of approximately one rhombomere in the val- compared to the wild-type embryo. ?rX? refers to the region of that remains between r4 and r7. (C-G) Confocal images of 5-day old wild-type (C,E,F) and val- (D,G) embryos in which the hindbrain reticulospinal neurons are visualized by retrograde filling with lysinated rhodamine-dextran. Anterior is to the top. The names of individually identifiable neurons are indicated. In wild-type embryos, the RoM3 neurons lie in r3, Mauthner (Mth) in r4, MiD2 in r5, MiD3 in r6 and CaD in r7. In val- embryos, the average distance from Mth to CaD is reduced by the length of approximately one rhombomere, and the MiD2 and MiD3 neurons lie close together in the region of one rhombomere?s length between r4 and r7. (EG) Higher power confocal images of MiD2 and MiD3 cells in wild-type (E,F) and mutant (G) embryos. Arrows indicate the long, unbranched lateral dendrite characteristic of the MiD2cm cell, while arrowheads indicate the shorter, branched lateral dendrite characteristic of the MiD3cm cell. Note that, although the MiD2cm and MiD3cm cells are immediately adjacent to one another in the mutant embryo shown in G, the MiD2cm cell is still anterior to the MiD3cm cell. (H,I) Sagittal sections of 56 h wild-type (H) and val- (I) embryos stained with the zn-5 antibody, which labels the putative motor nuclei of the abducens nerve (VI) in rhombomeres 5 and 6. Anterior is to the left. These motor nuclei are largely absent in the val- embryo. The putative abducens motor nuclei differentiate relatively late during hindbrain development, since they first stain with zn-5 24 hours later than do the earlier differentiating hindbrain commissural neurons (Trevarrow et al., 1990). Scale bars, (A,B) 50 μm; (C,D) 50 μm; (E-G) 20 μm; (H,I) 20 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development