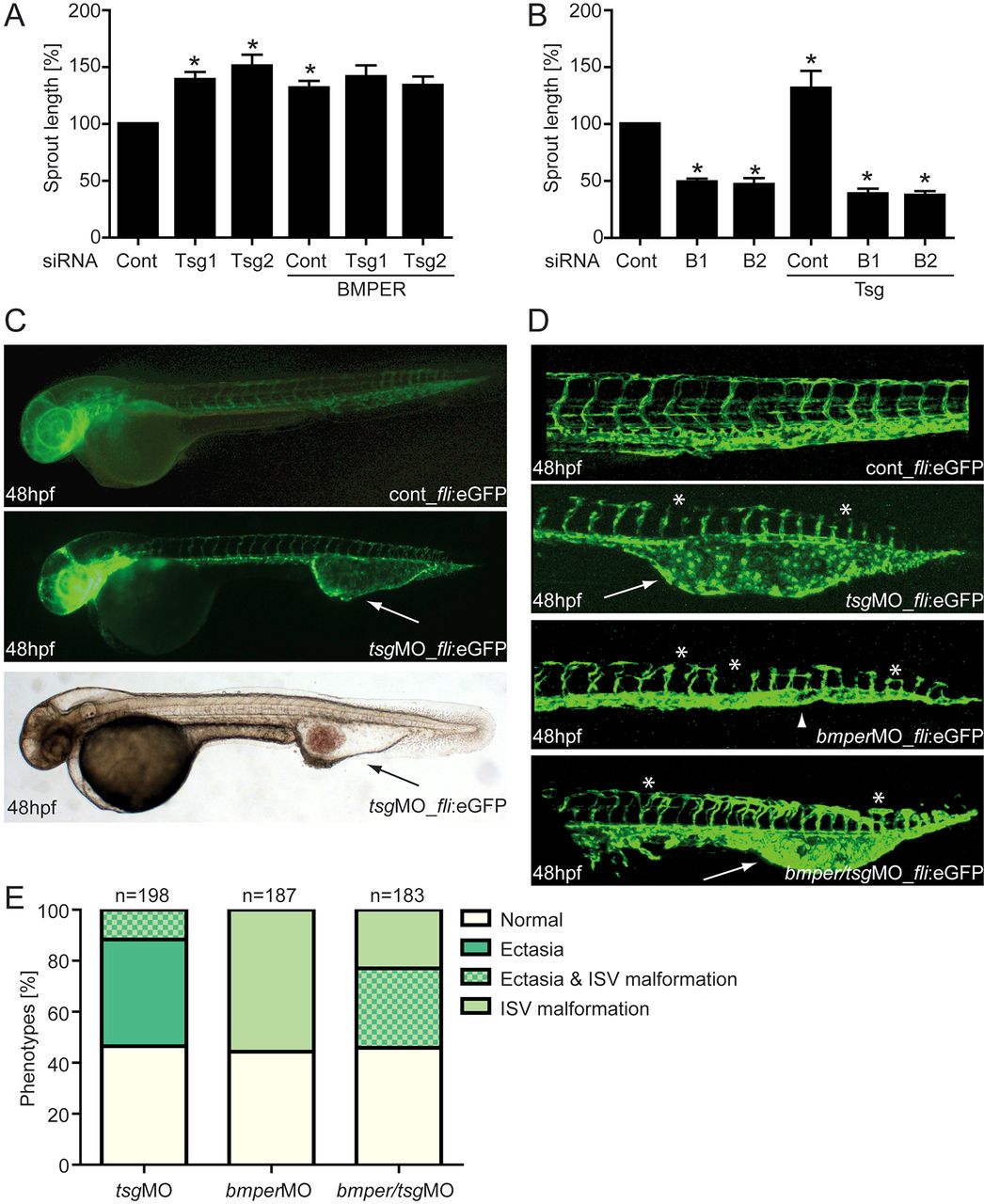
Fig. 8
The BMP modulators BMPER and Tsg are necessary for proper angiogenesis in vitro and in zebrafish development. HUVECs were transfected with either Tsg- or BMPER-specific siRNAs, or with scrambled siRNA as a control. Thereafter, Tsg- or BMPER-silenced HUVECs were stimulated with BMPER and Tsg, respectively, and subjected to the tube formation assay. (A) Cumulative sprout length of Tsg-silenced HUVECs stimulated with BMPER and (B) cumulative sprout length of BMPER-silenced HUVECs stimulated with Tsg. Values are means ± s.e.m.; n = 3; *P<0.01 versus siRNA control. (C?E) Silencing of Tsg in zebrafish embryos causes malformations during blood vessel development. (C) Vasculature morphology of uninjected (top) and 0.125mM Tsg MO-injected (middle) tg(fli1:eGFP) fish embryos at 48hpf with formation of a large venous malformation (white arrows). (Bottom) Overall morphology of Tsg MO-injected zebrafish at 48hpf with blood accumulation in the ventral tail vein ectasia (black arrow). (D) Formation of the trunk vasculature in 48hpf tg(fli1:eGFP) fish embryos after injection of 0.125mM Tsg or 0.25mM BMPER MO or a combination of both. Tsg morphants displayed ventral tail vein ectasia (white arrows) and some disruption of ISVs and the DLAV (asterisks). In BMPER morphants disruption of ISVs and DLAV was more pronounced and in addition loss of the CVP (arrowhead) was observed. Double morphants displayed the malformations of both single Tsg/BMPER morphants. (E) Quantification of vascular defects in 48hpf tg(fli1:eGFP) Tsg and BMPER morphants. CVP, caudal vein plexus; DLAV, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; ISV, intersomitic vessels; hpf, hours post-fertilisation; MO, morpholino oligonucleotide.