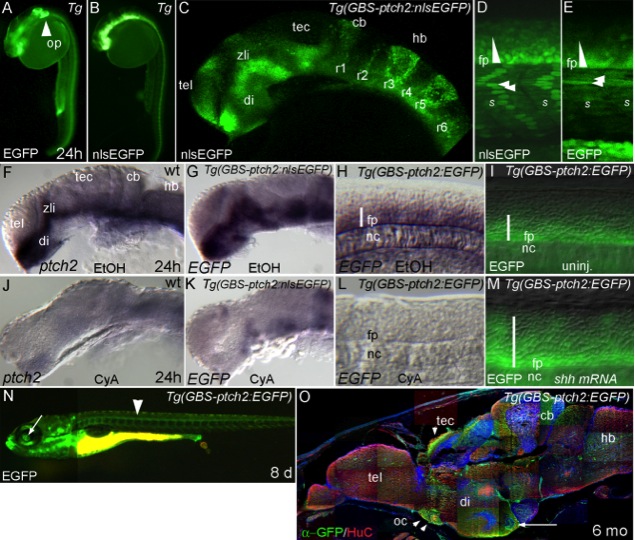
Fig. 4 Transgenic zebrafish lines that report Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. A,B: Live 24 hours postfertilization (hpf) embryos imaged using a fluorescent dissecting microscope. The Tg(GBS-ptch2:EGFP) (A) and Tg(GBS-ptch2:nlsEGFP) (B) lines accurately report Hh signaling in responding tissues of the floor plate, ventral brain, and somites. Only the (Tg(GBS-ptch2:EGFP) line has inappropriate green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in the otic placode (A, arrowhead). C: Confocal image of the head of an nlsEGFP expressing embryo showing expression in Hh responsive regions of the brain (compare with ptch2 in situ labeling in F). D,E: Confocal images of the trunk region in live 24 hpf nlsEGFP (D) and enhanced GFP (EGFP) (E) transgenic embryos show appropriate nuclear or cytoplasmic GFP labeling (arrowheads). GFP intensity in the spinal cord allows visualization of the ventral-to-dorsal Shh signaling gradient (triangles) (Stamataki et al., 2005). More laterally, GFP is expressed in Hh responsive slow muscle fibers (arrowheads). F: Shh responsive regions of the brain visualized by ptch2 ISH. G,H: In situ labeling for GFP mRNA is the same as the known ptch2 expression pattern in the brain (G) and trunk (H). I: GFP expression in the spinal cord and somites in an uninjected Tg(GBS-ptch2:EGFP) embryo. J?L: ptch2 and GFP mRNA expression are eliminated when embryos are treated with the Hh signaling inhibitor cyclopamine (Incardona et al., 1998). M: Dorsally expanded GFP expression following injection of Shha encoding mRNA. N: GFP expression in a live 8-day-old Tg(GBS-ptch2:EGFP) larvae includes the floor plate (arrowhead) and retinal ganglion cell axons of the eye (arrow). O: Sagittal section through the brain of a 6-month-old Tg(GBS-ptch2:EGFP) adult co-labeled to show neurons (HuC/D antibody) and nuclei (dapi). Retinal ganglion cell axons express EGFP in the optic chiasm and where they terminate in the tectum (arrowheads). Ventricular regions of the brain continue to be Hh responsive in adults (arrow). cb, cerebellum; di, diencephalon; fp, floor plate; hb, hindbrain; nc, notochord; oc, optic chiasm; op, otic placode; r, rhombomere; s, somite; tec, tectum; tel, telencephalon; zli, zona limitans interthalamica.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.