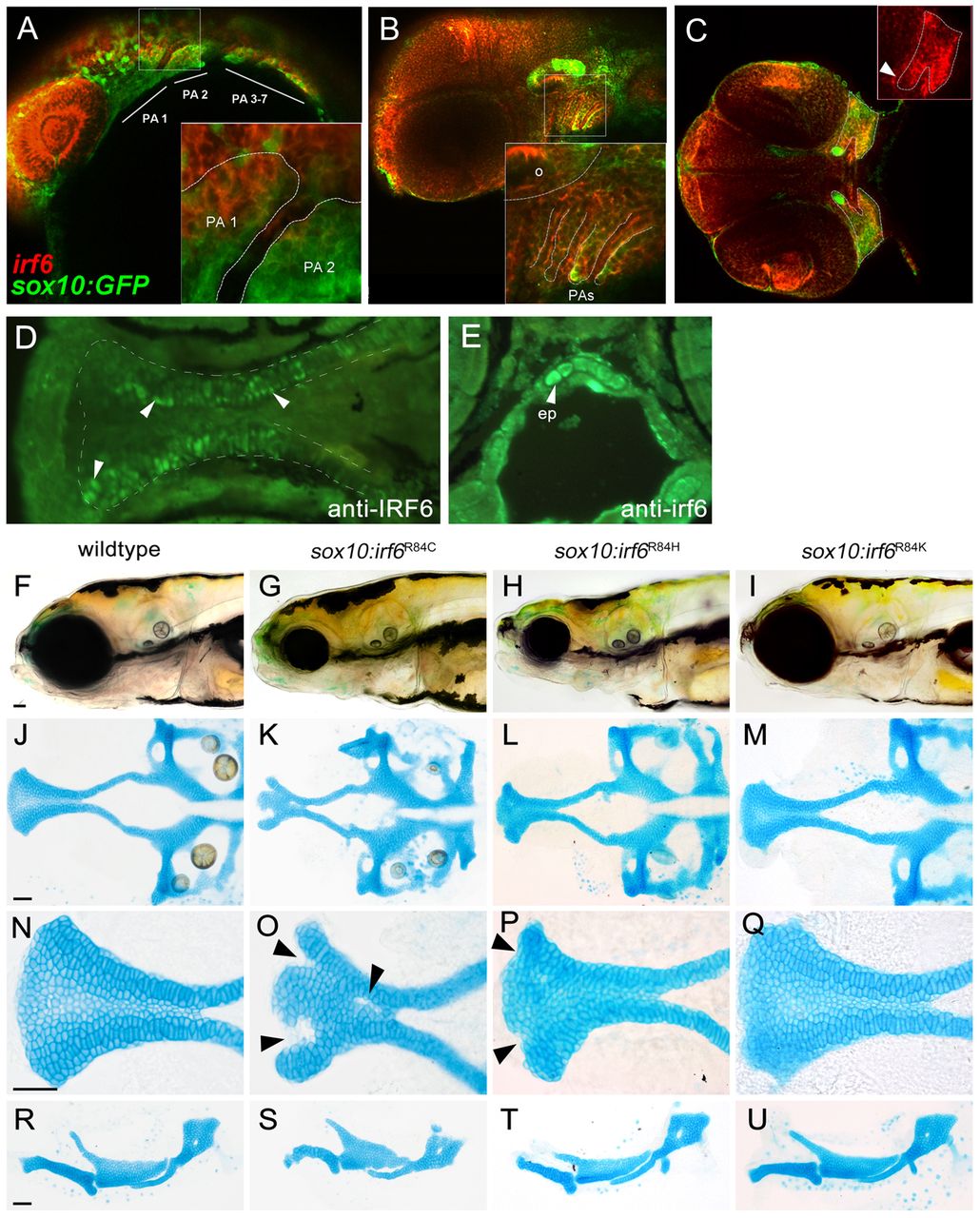
Fig. 3 Expression analysis of endogenous irf6 and functional analysis of sox10:irf6R84C,H,K mutants. (A-E) RNA in situ hybridization demonstrated extensive overlap of endogenous irf6 expression with sox10-labeled CNCCs. (A) At 24 hpf, irf6 expression can be found pharyngeal arches. (B) By 48 hpf, irf6 expression is detected in both the pharyngeal mesenchyme and pharyngeal ectoderm. (C) By 55 hpf, irf6 expression is detected in the converging maxillary and mandibular prominences (inset). (D,E) Immunohistochemistry at 72 hpf using antisera against non-overlapping epitope of human IRF6 (D) and zebrafish irf6 (E), each with specific staining in the ethmoid plate, shown in ventral and cross-sectional views. Arrowheads indicate ethmoid plate chondrocytes. (F-Q) Comparison of wild-type and mutant craniofacial structures, with live images (F-I), dissected neurocranium (J-M), flat-mounted lower jaw structures (R-U) at 10× magnification and ethmoid plate (N-Q) at 40× magnification. The R84C cleft phenotype is the most severe (arrowheads, O). R84H has a milder cleft phenotype, with subtle indentations at the anterior edge of the seam between median and lateral ethmoid (arrowheads, P), whereas the conserved amino acid substitution R84K appears wild type. ep, ethmoid plate; PA, pharyngeal arch; o, otic vesicle.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development