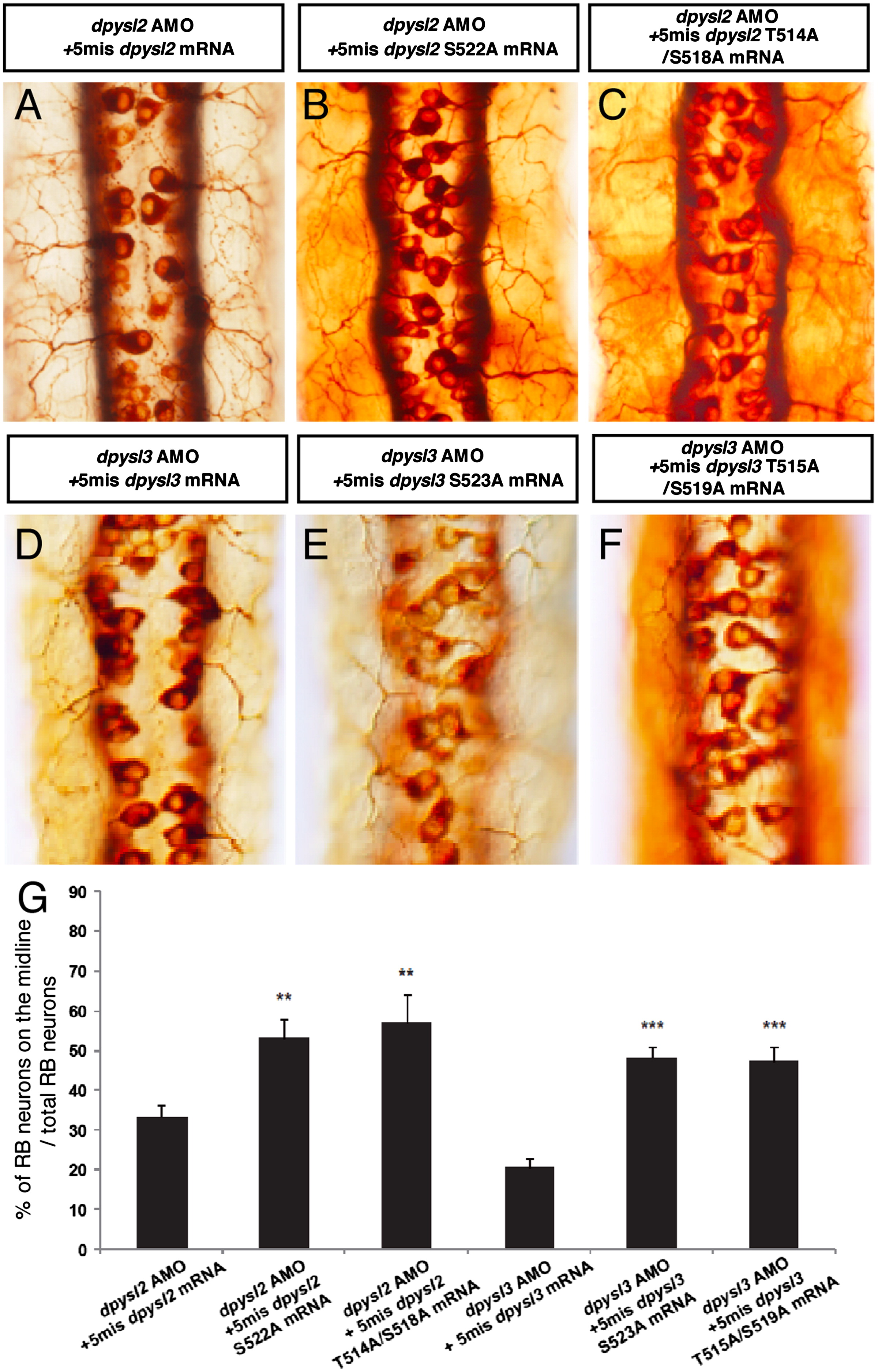
Fig. 2 The inhibition of phosphorylation of Dpysl2 and Dpysl3 caused the abnormal positioning of Rohon-Beard neurons. (A?F) The position of RB neurons in the dpysl2 morphants (A?C) and the dpysl3 morphants (D?F) which were co-injected with various AMO-resistant (5-mis) mRNAs at 28 hpf. Dorsal view, anterior top. The morphants which co-injected with mutant mRNAs showed severe positioning defects in RB neurons (B, C, E, F) compare to the normal mRNA co-injected morphants (A, D). (G) Quantitative data for the percentage of RB neurons on the midline. Data are mean ± SEM; NNP<0.01, NNNP<0.001, different from the normal mRNA co-injected morphants using 2-tailed paired Student′s t-test.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 370(2), Tanaka, H., Morimura, R., and Ohshima, T., Dpysl2 (CRMP2) and Dpysl3 (CRMP4) phosphorylation by Cdk5 and DYRK2 is required for proper positioning of Rohon-Beard neurons and neural crest cells during neurulation in zebrafish, 223-236, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.