Fig. S1
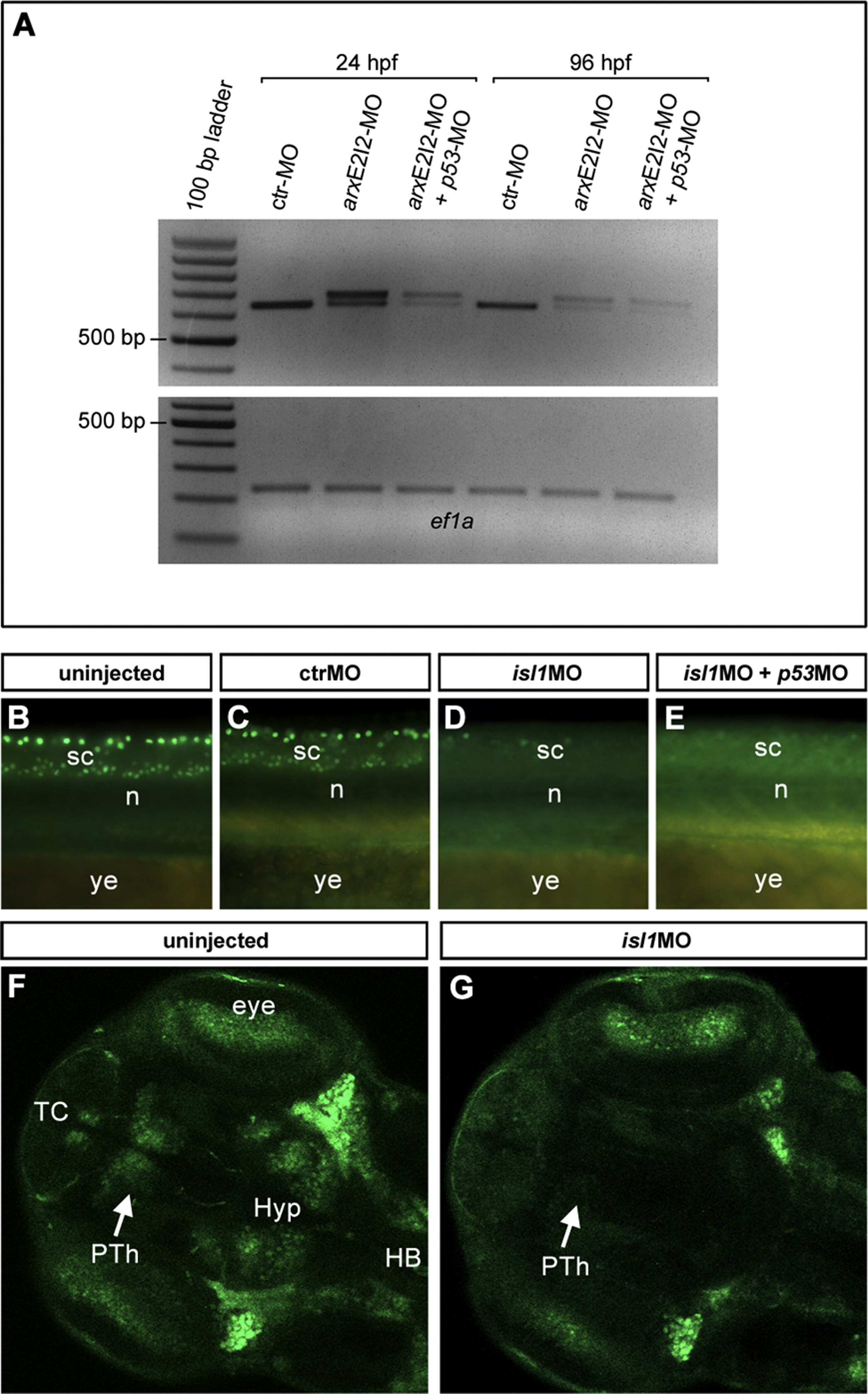
Assessment of arxE2I2-MO (A) and isl1E2-MO (B-G) efficiency. (A) PCR on cDNA synthesized from 24 and 96 hpf embryos injected with 8 ng of arxE2I2-MO. This morpholino blocks the splice donor site at the exon2-intron2 boundary, giving rise to a longer mature mRNA. We amplified elongation factor 1-alpha (ef1a) as a positive control.
(B-G) Anti-Isl1 immunohistochemistry on embryos injected with 8 ng of isl1E2-MO. At 24 hpf (B-E) little or no Isl1 protein was detectable in the spinal cord of morphant embryos (D,E) compared to controls (B,C), validating the efficiency of the knock-down. At 72 hpf (F,G), the degree of Isl1-immunoreactivity in the brain was very much reduced in the morphants (G) compared to uninjected embryos (F), although it was still detectable in regions of high isl1 expression. The white arrows point to the prethalamus, where group 1 DA neurons develop. Abbreviations: n, notochord; PTh, prethalamus; sc, spinal cord; TC, telencephalon; ye, yolk extension.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 369(1), Filippi, A., Jainok, C., and Driever, W., Analysis of transcriptional codes for zebrafish dopaminergic neurons reveals essential functions of Arx and Isl1 in prethalamic dopaminergic neuron development, 133-149, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.