Fig. 7
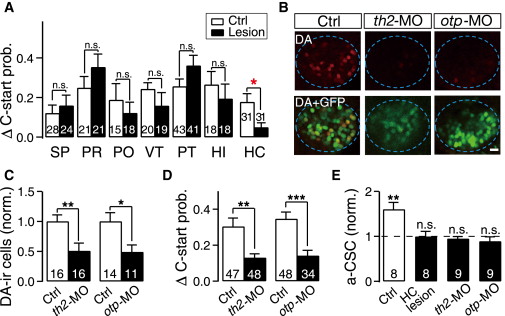
Dopaminergic Neurons in the Caudal Hypothalamus Are Required for the Visual Modulation of Audiomotor Functions (A) Effects of two-photon laser focal lesion of specific dopaminergic neuron clusters on preceding flash-induced increases in the probability of sound-evoked C-start behavior. The open and filled bars represent data obtained from larvae without or with laser lesion, respectively. The numbers on the bars represent the numbers of ETvmat2:GFP larvae examined. (B and C) Examples (B) and summary (C) of data showing that morpholino oligo (MO)-based knockdown of th2 (th2-MO) or both otp a and otp b (otp-MO) reduces the number of DA-immunoreactive (DA-ir) neurons in the HC. Top in (B), DA-ir signal; Bottom in (B), merged DA-ir and GFP-ir signals. The blue dashed circles represent HC position. The images in (B) were taken from one optic section with a thickness of <4 μm. Scale represents 10 μm. (D) Effects of th2 knockdown and otp a and otp b co-knockdown on preceding flash-induced increases in the probability of sound-evoked C-start behavior. (E) Summary of data showing the effects of focal HC lesion, th2 knockdown, and otp a and otp b co-knockdown on preceding flash-induced enhancement of Mauthner cell a-CSCs. n.s., no significance; p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; p < 0.001 (paired Student?s t test for M-cell recording data and unpaired Student?s t test for behavior data). Error bars indicate SEM. See also Figures S5 and S6.