Fig. S2
Related to Figure 3. Quantification of the fluid-jet stimulus at 2 dpf and 5 dpf.
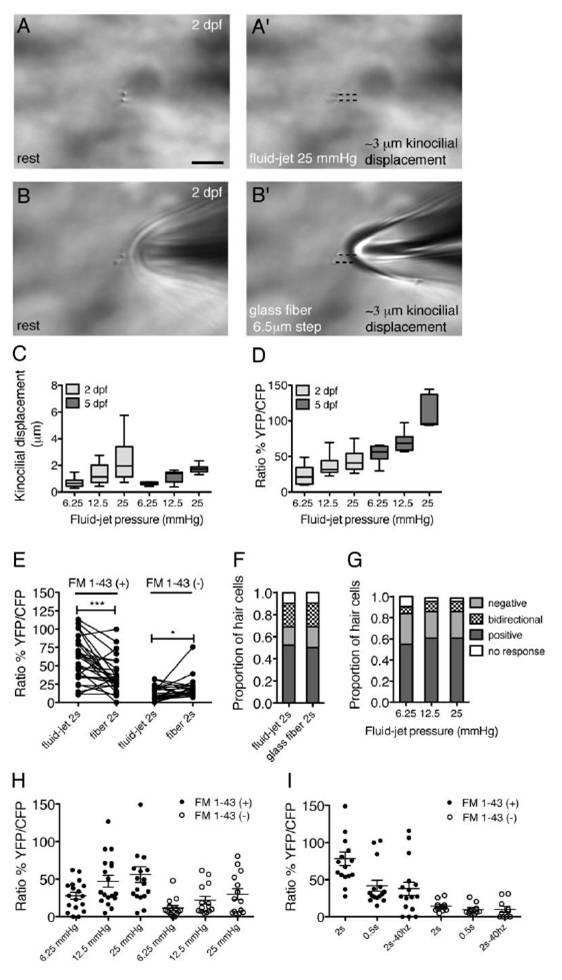
(A-B′) Visual confirmation of stimulus delivered to same neuromast at 2 dpf. The measured displacement of kinocilial tips can be visually confirmed using a fluid-jet (A, A′) or a glass fiber (B, B′). Black dashed lines indicate the displacement of kinocilial tips. (C) Average kinocilial displacement per neuromast with increasing water pressure at 2 and 5 dpf (2 dpf n = 17 neuromasts, 5 dpf n = 7 neuromasts). (D) Average calcium response per neuromast for the same stimuli as in (C) (n = 6 neuromasts). (E) Calcium response of individual hair cells at 2 dpf to sustained, 2 s fluid-jet stimulation, compared to a sequential, sustained 2 s glass fiber stimulus (n = 53 hair cells). Both FM 1-43 (+) and FM 1-43 (-) hair cells responded to each type of stimulus, although overall the fluid-jet stimulated hair cells more robustly. (F) Sequential stimulation using a glass fiber and fluid-jet yielded the same proportions of bi-directional, positive and negative responses at 2 dpf (n = 53 hair cells). (G) Proportion of types of responses in hair cells at 2 dpf using three fluid-jet pressures (n = 31 hair cells). (H) At 2 dpf, both FM 1-43 (+) hair cells (solid circles), and FM 1-43 (-) hair cells (open circles) (n = 17 and 14 hair cells respectively) responded to a 2s stimulus at all levels of fluid-jet pressures tested. (I) In addition to a 2 s step, at 2 dpf, FM 1-43 unlabeled hair cells responded to a 0.5 s step and a 2 s, 40 hz square wave (n = 26 hair cells). Error bars in (H and I) represent s.e.m. Whiskers in (C and D) represent 10th and 90th percentile. Scale bar in (A) is 5 μm. * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 23(2), Kindt, K.S., Finch, G., and Nicolson, T., Kinocilia mediate mechanosensitivity in developing zebrafish hair cells, 329-341, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell