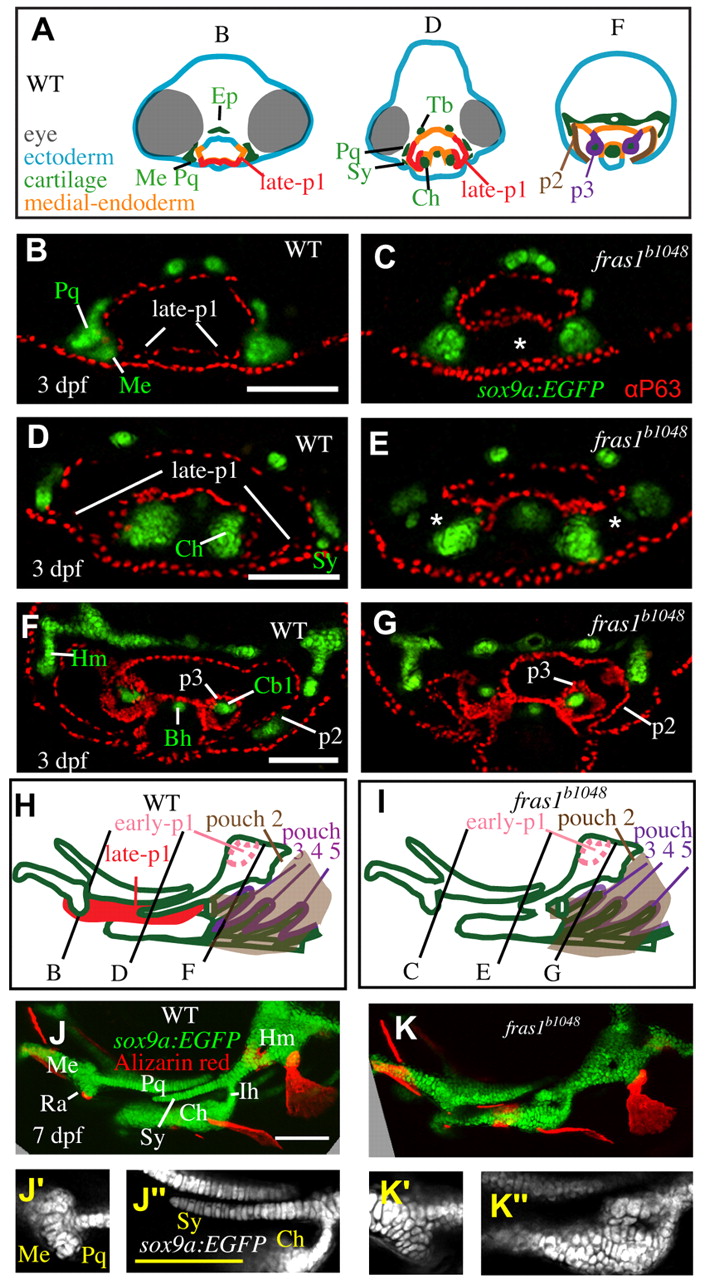
Fig. 2 Skeletal elements near late-p1 are affected by fras1 mutation. (A) Illustrations of WT epithelia and cartilage on transverse sections, shown dorsal up. Ep, ethmoid plate; Tb, trabecula. (B-G) Tissue sections labeled with anti-P63 and sox9a:EGFP, taken from the section level of (B,C) Meckel′s-palatoquadrate joint, (D,E) symplectic cartilage, and (F,G) opercular flap. By 72 hpf, fras1 mutants exhibit loss (asterisk) of late-p1 (B-E) but not p2 or p3 (F,G) derivatives. (H,I) Illustrations of 7-dpf cartilaginous skeletons, showing how pouch derivatives intersect with cartilages and how the sections shown in B-G map onto 7-dpf skeletons; shown anterior to left, dorsal up. (J-K′′) Confocal projections of live-imaged fish showing bone (Alizarin Red staining) and cartilage (sox9a:EGFP expression). Dermal bone morphology typically resembles WT (J) in fras1 mutants (K), although mild opercle bone defects are sometimes found in fras1 mutants (not shown). Inset confocal sections highlight morphology at first arch-derived (J′,K′ ) and second arch-derived (J′′,K′′) joint regions. Fully expressive fras1 mutants display distinct cartilage defects including (K′) M-Pq fusion and (K′′) Sy-Ch fusion with short Sy. Arch 1-derived cartilages: Me, Meckel′s cartilage; Ra, retroarticular process of Meckel′s cartilage; Pq, palatoquadrate. Arch 2-derived cartilages: Cb1, first ceratobranchial cartilage; Ch, ceratohyal; Ih, interhyal; Hm, hyomandibular; Sy, symplectic. Scale bars: 100 μm (applicable to each row).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development