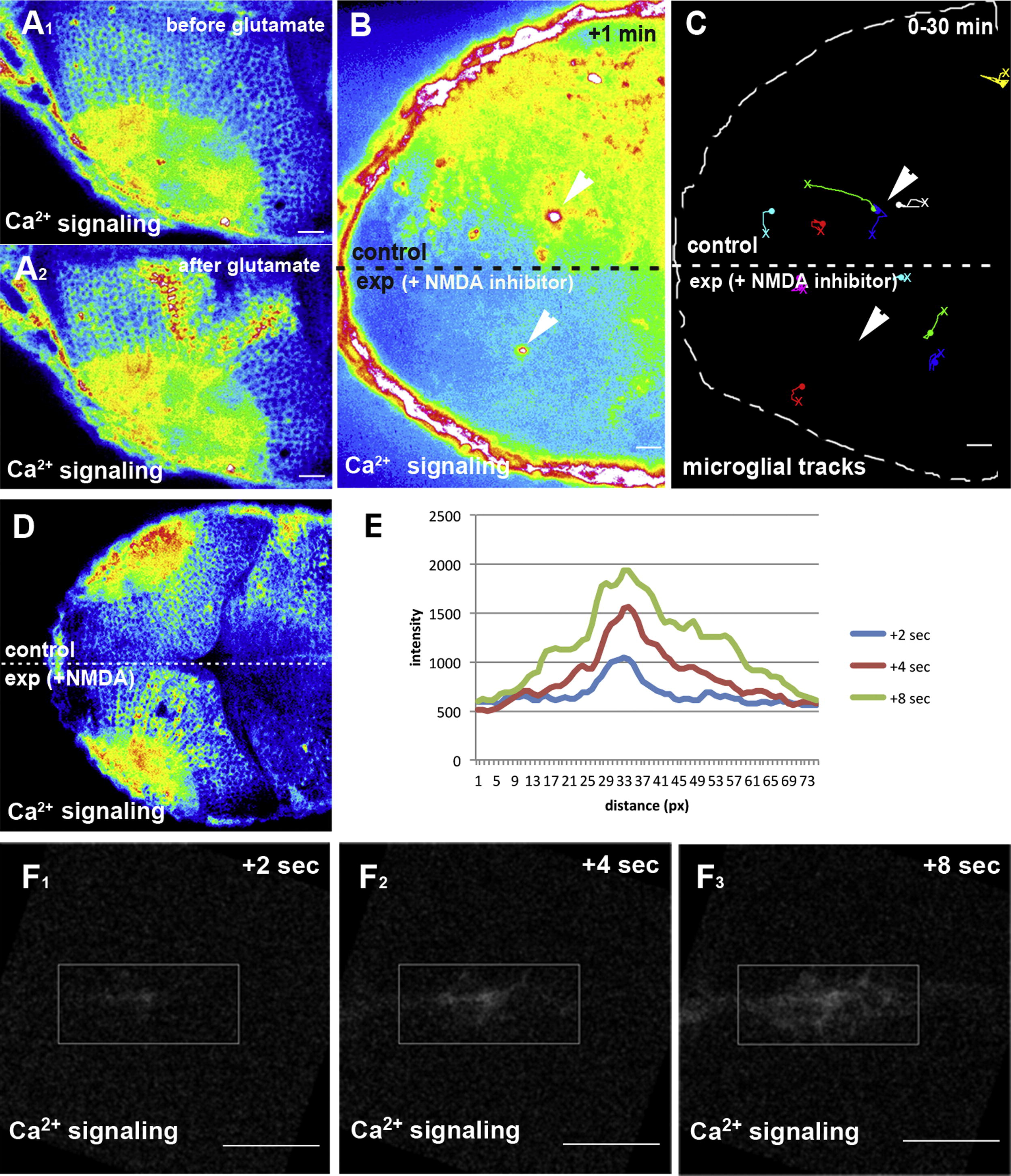
Fig. 6 Glutamate Promotes Ca2+ Signaling and Microglial Movement(A) Ca2+ signaling (beta-actin::GCAMP3.1) before (A1) and after (A2) injection of glutamate.(B) Single-lobe injection (exp) of NMDA inhibitors blocks Ca2+-wave (beta-actin::GCAMP3.1) formation upon laser injury. Laser ablation sites are marked by white arrowheads.(C) Microglial tracking in the same NMDA-inhibitor-injected embryo as in (B). Laser ablation sites are marked by white arrowheads. The starting point of individual tracks is marked with an X and the end point with a dot.(D) Single-lobe injection (exp) of NMDA induces Ca2+-wave (beta-actin::GCAMP3.1) formation.(E) Intensity plot of the Ca2+ signal upon NMDA uncaging measured 2 s, 4 s, and 8 s after uncaging within the ROI shown in (F).(F) Ca2+ signaling (beta-actin::GCAMP3.1) 2 s (F1), 4 s (F2), and 8 s (F3) after uncaging of NMDA (Movie S11, upper left).Scale bars for all images: 20 μm. All images were produced using an Andor Spinning Disk Confocal with a 20×/NA0.7 objective.See also Movies S9, S10, and S11.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(6), Sieger, D., Moritz, C., Ziegenhals, T., Prykhozhij, S., and Peri, F., Long-Range Ca(2+) Waves Transmit Brain-Damage Signals to Microglia, 1138-1148, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell