Fig. 4
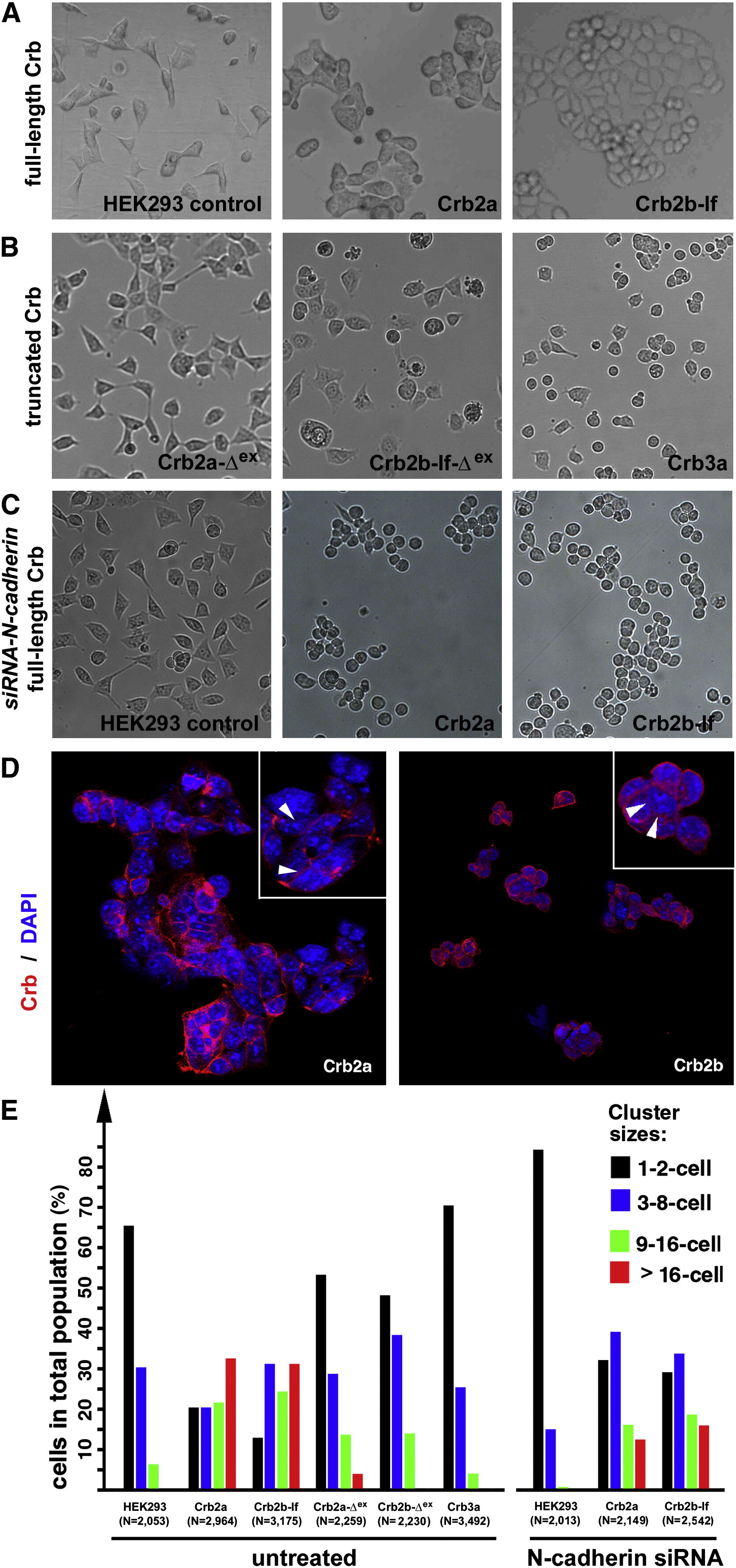
The Extracellular Domains of Crb2a- or Crb2b-lf-Mediated Cell Aggregation in HEK Cells (A) Unlike wild-type HEK cells, it is more common for monoclonal HEK cells that express full-length Crb2a or Crb2b-lf to grow in large aggregates. (B) Expression of Crb3a, Crb2a-Δex, and Crb2b-Δex, which lack typical Crb extracellular domains, did not prompt HEK cell aggregation. (C) Suppression of N-cadherin by N-cadherin siRNA treatment further reduced the tendency for wild-type HEK cells to form aggregates, suggesting that the low-level cell-cell adhesion in wild-type HEK cells was dependent on N-cadherin. However, loss of N-cadherin did not prevent Crb2a- or Crb2b-lf-expressing HEK cells from aggregating, suggesting that the Crb2-mediated cell-cell adhesion was independent of N-cadherin. (D) Crb2a and Crb2b-lf localized to the cell membrane in HEK cells with various degrees of enrichment at the cell-cell junctions (arrowheads, insets). The cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (E) To quantitatively evaluate the adhesion property of the extracellular domain of Crb proteins, various Crb-expressing HEK cells were counted and categorized according to their cluster sizes. The total numbers of cells are indicated below the histograms. The symbol Δex indicates that the extracellular domain of the corresponding Crb protein was deleted (Figure 6A). See also Figure S3.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 22(6), Zou, J., Wang, X., and Wei, X., Crb Apical Polarity Proteins Maintain Zebrafish Retinal Cone Mosaics via Intercellular Binding of Their Extracellular Domains, 1261-1274, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell