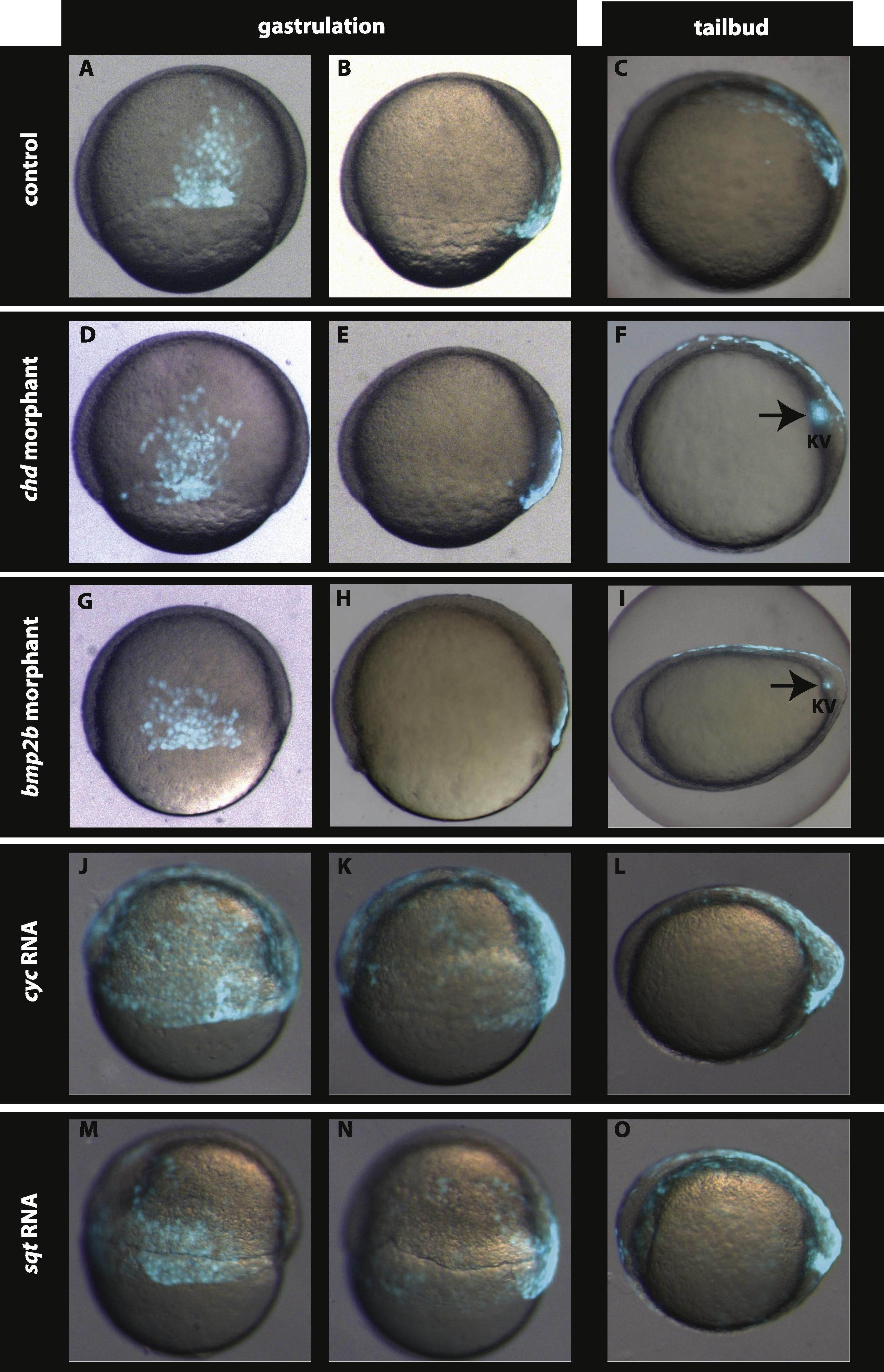
Fig. 3
Nodal signalling is involved but Chordin–BMP signalling is dispensable in setting up the dorsal EVL (dEVL) GFP domain. Compared to the control (A and B), the GFP labelled dEVL domain is neither altered in chd morphants (D and E) nor in bmp2b morphants (G and H). Interestingly, over-expression of nodal related ligands cyc (J and K) and sqt (M and N) leads to expansion of the dEVL as well as the dorsal forerunner cells. At tail-bud stage the GFP expression is restricted to the dorsal periderm and the Kupffer’s vesicle in control embryos (C). This GFP expression is not altered in chd (F) and bmp2b morphants (I) whereas expansion of the GFP domain in the periderm and in Kupffer’s vesicle are observed in embryos over-expressing cyc (L) and sqt (O). A, D, G, J, and M dorsal view at 60–70% epiboly. B, E, H, K, and N lateral view at 60–70% epiboly. Dorsal is to the right. C, F, I, L, and O lateral view, anterior is to the left.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 129(1-4), Chen, Y.Y., Harris, M.P., Levesque, M.P., Nüsslein-Volhard, C., and Sonawane, M., Heterogeneity across the dorso-ventral axis in zebrafish EVL is regulated by a novel module consisting of sox, snail1a and max genes, 13-23, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.