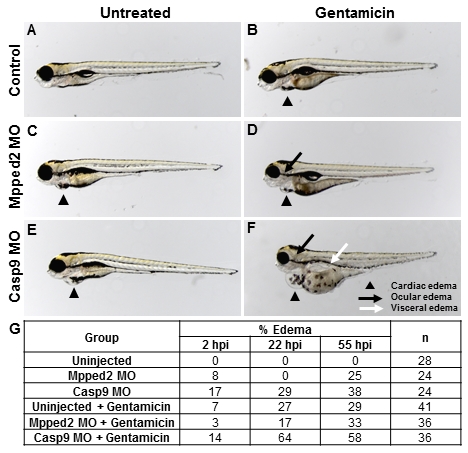
Fig. S9
Casp9 and mpped2 knockdown embryos are more susceptible to gentamicin-induced kidney injury. Compared to control embryos (A), casp9 and mpped2 knockdown embryos develop edema at 103 hpf (C, E), suggestive of a renal defect. When injected with gentamicin, a nephrotoxin that reproducibly induces edema in control embryos (B), mpped2 and casp9 knockdown embryos develop edema earlier, more frequently, and in a more severe fashion (D, F). Whereas control embryos primarily develop cardiac edema, mpped2 and casp9 knockdown embryos display cardiac (arrowhead), ocular (black arrow), and visceral (white arrow) edema, demonstrating that mpped2 and casp9 knockdown predisposes embryos to kidney injury. (G) Quantification of edema prevalence in control, mpped2, and casp9 knockdown embryos 2, 22, and 55 hours post-injection (hpi) of gentamicin. These numbers are presented graphically in Figure 2X.