Fig. 3
Defects of exocrine pancreas formation in both morha4/ha4 and Ddx46hi2137/hi2137 mutants are rescued by the overexpression of Ddx46 mRNA but not mutated Ddx46 mRNA.
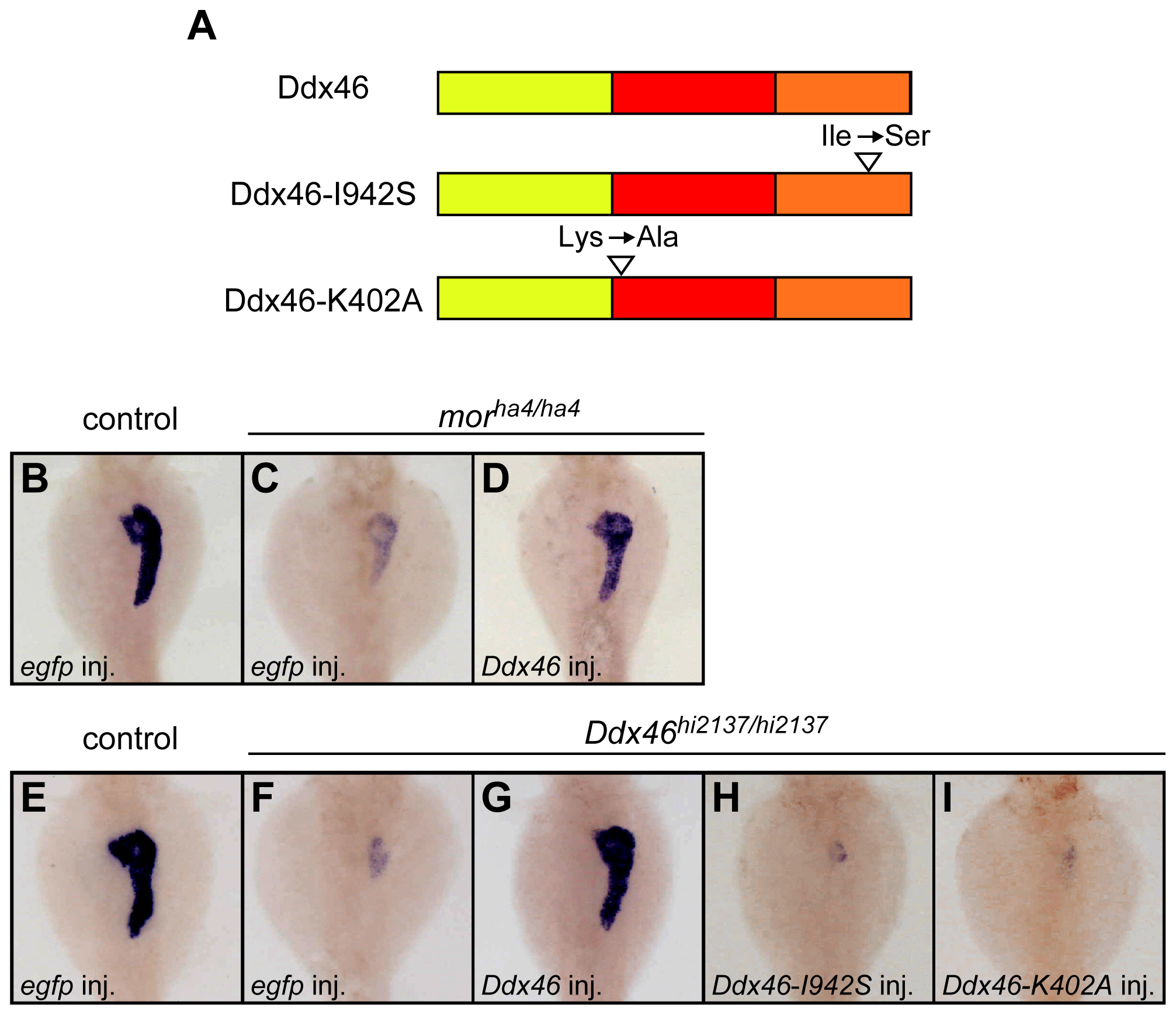
(A) Scheme of the Ddx46 protein structure. The yellow, red, and orange boxes indicate the N-terminal, DEAD-box helicase, and C-terminal domain, respectively. Mutations were introduced into the Ddx46 protein; in Ddx46-I942S, an isoleucine in the C-terminal domain of Ddx46 was changed to serine, which is the same mutation as that in the morha4 mutant; in Ddx46-K402A, GKT in motif I, which is important for ATPase activity in Ddx46 homologues, was changed to GAT. (B?I) All dorsal views, anterior to the top. The expression of try, a molecular marker for the exocrine pancreas, was examined using whole-mount in situ hybridization at 3.5 dpf. The try expression in the exocrine pancreas was markedly reduced in egfp mRNA-injected morha4/ha4 (C) and Ddx46hi2137/hi2137 mutants (F) compared to egfp mRNA-injected control larvae (B, E). The try expression was rescued in the Ddx46 mRNA-injected morha4/ha4 (D) and Ddx46hi2137/hi2137 mutants (G), whereas no rescue was achieved by the overexpression of Ddx46-I942S (H) or Ddx46-K402A (I) mRNA into Ddx46hi2137/hi2137 mutants. Control larvae-sibling WT or morha4/+ larvae (B?D), sibling WT or Ddx46hi2137/+ larvae (E?I)-had normal phenotypes.