Fig. 2
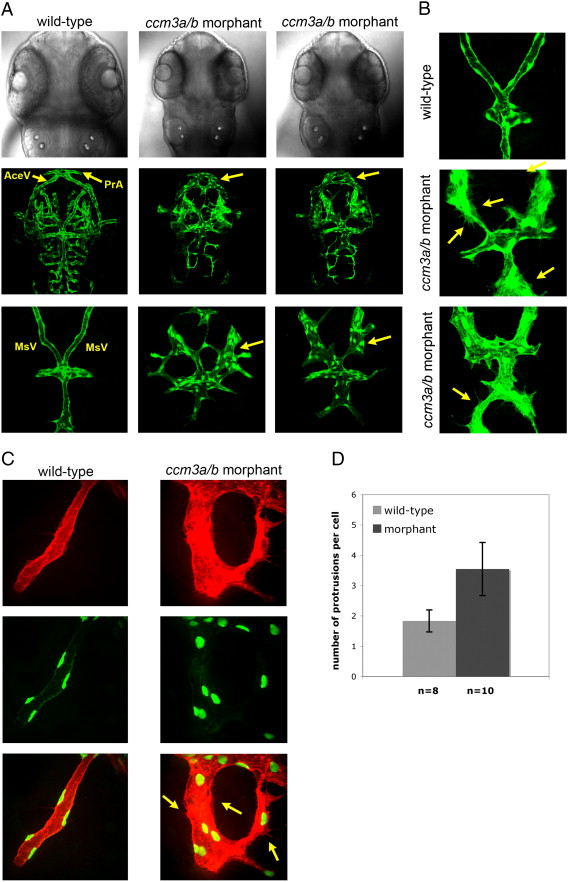
Morpholino knockdown of ccm3a/b causes gross dilation and mispatterning of cranial vessels. (A) At 54 hpf, confocal z-stack projections of dorsal head vasculature showed enlargements in the prosencephalic arteries (PrA), mesencephalic veins (MsV), and anterior cerebral veins (AceV) in embryos injected with 0.75 ng ccm3a/b morpholino (> 90%, n = 62). (B) Morpholino knockdown of ccm3a/b results in greater number of protrusions evident in endothelial cells of the dilated cranial vasculature (yellow arrows). (C) MsVs of the wildtype and ccm3a/b morphant embryos imaged at higher magnification in kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry; fli1:nlsEGFP transgenic background. (D) ccm3a/b morphant embryos have a significantly higher number of cell protrusions per endothelial cell compared to wildtype (p-value < 0.01, n refers to number of embryos analyzed, with 3?5 cells counted per embryo).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 362(2), Yoruk, B., Gillers, B.S., Chi, N.C., and Scott, I.C., Ccm3 functions in a manner distinct from Ccm1 and Ccm2 in a zebrafish model of CCM vascular disease, 121-131, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.