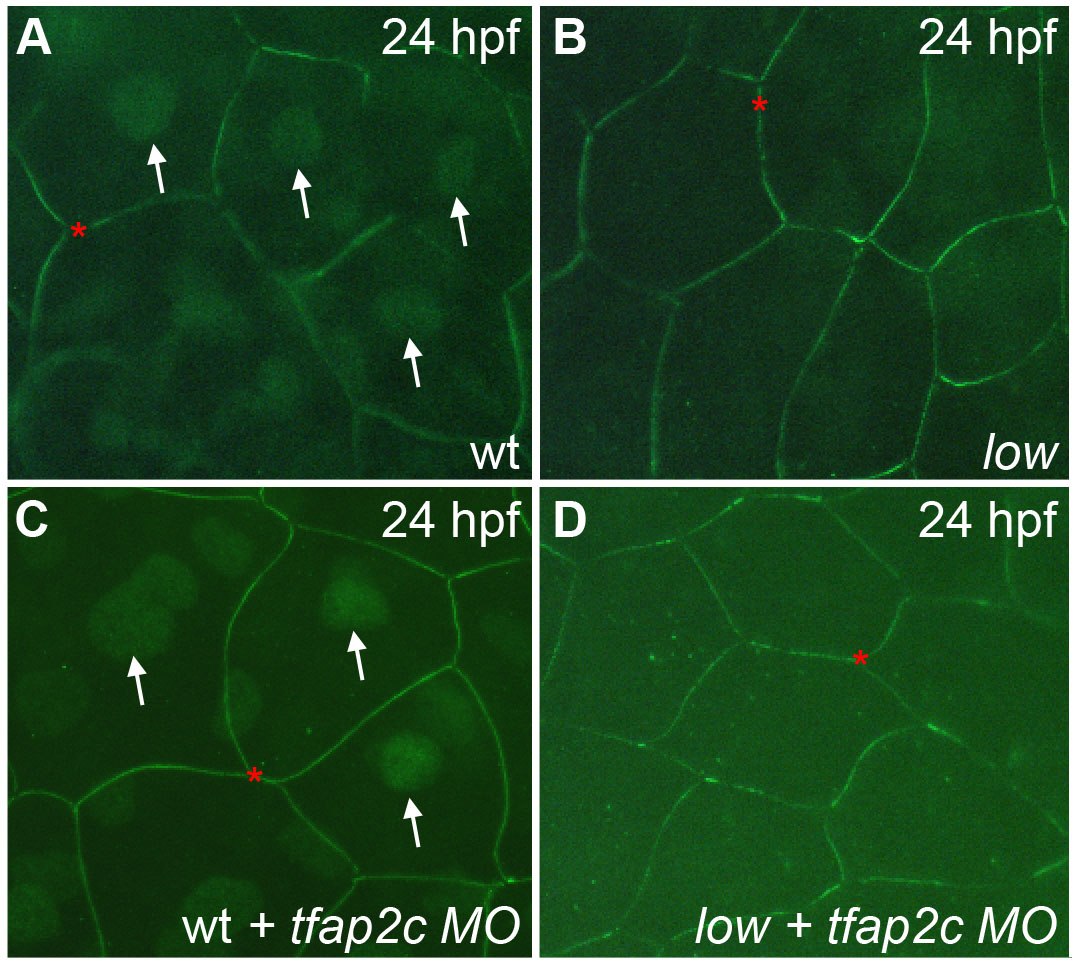
Fig. S5
Nuclear anti-Tfap2a immunoreactivity is specific for Tfap2a protein. (A-D) Lateral views of cells of the enveloping layer (EVL), covering the yolk of 24 hpf embryos fixed and processed to reveal anti-Tfap2a immunoreactivity (IR). (A,C) Wild-type and (B,D) presumed tfap2a mutant embryos that are either (A,B) uninjected or (C,D) injected with MO targeting tfap2c. (A,C) In wild-type embryos, anti-Tfap2a IR is visible in nuclei (arrows) and at cell boundaries (red asterisks). (B) Presumed tfap2a mutants lack nuclear staining. Cell boundary staining persists, suggesting that it is non-specific. In (C) wild-type embryos injected with a tfap2c MO, nuclear anti-Tfap2a IR persists, suggesting that anti-Tfap2a is specific to Tfap2a and does not recognize Tfap2c. (D) A presumed tfap2a mutant injected with tfap2c MO.