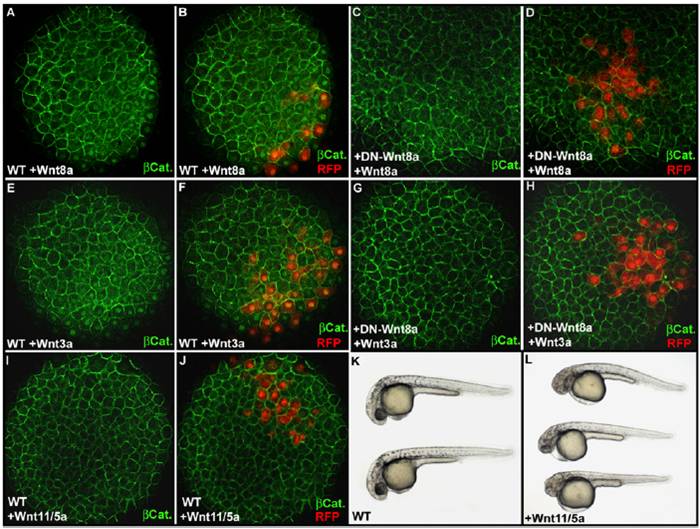
Fig. S4 Effect of ectopic expression of Wnt8a, Wnt3a, and Wnt11/5a on the intracellular localization of β-catenin as revealed by immunofluorescence. Immunofluorescence localization of β-catenin at 3 hpf (high stage) at the animal pole of an embryo injected with 10 pg of Wnt8a (A) or Wnt3a (E) mRNA together with 50 pg of red fluorescent protein (RFP) mRNA in one animal pole blastomere at the 64-cell stage. (B and F) Overlay of the green channel, for visualization of β-catenin, and the red channel, for visualization of cells expressing the RFP and secreting Wnt8a or Wnt3a, reveals the activation of the maternal β-catenin signaling pathway (accumulation of β-catenin into the nucleus) at a distance up to three cell diameters from cells secreting Wnt8a (B) or Wnt3a (F). Injection of 500 pg DN-Wnt8a mRNA at the one-cell stage prevents stimulation of the maternal β-catenin signaling pathway by Wnt8a (C and D) or Wnt3a (G and H). (I and J) In the same experimental conditions, injection of a mix of 200 pg of Wnt11 mRNA and 200 pg of Wnt5a mRNA fails to activate the maternal β-catenin signaling pathway and does not induce nuclear accumulation of β-catenin in animal pole blastomeres within or at the vicinity of the Wnt11/Wnt5a secreting clone. (L) Injection of the same mix of 200 pg of Wnt11 mRNA and 200 pg of Wnt5a mRNA at the one-cell stage induces cyclopia phenotypes characteristic of overexpression of noncanonical Wnts, demonstrating that translation from these mRNAs produces active Wnt proteins. (K) Wild-type embryo. Embryos in A?J are in animal pole view. Embryos in K and L are at 30 hpf and are in lateral view anterior to the Left and dorsal to the Top.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA