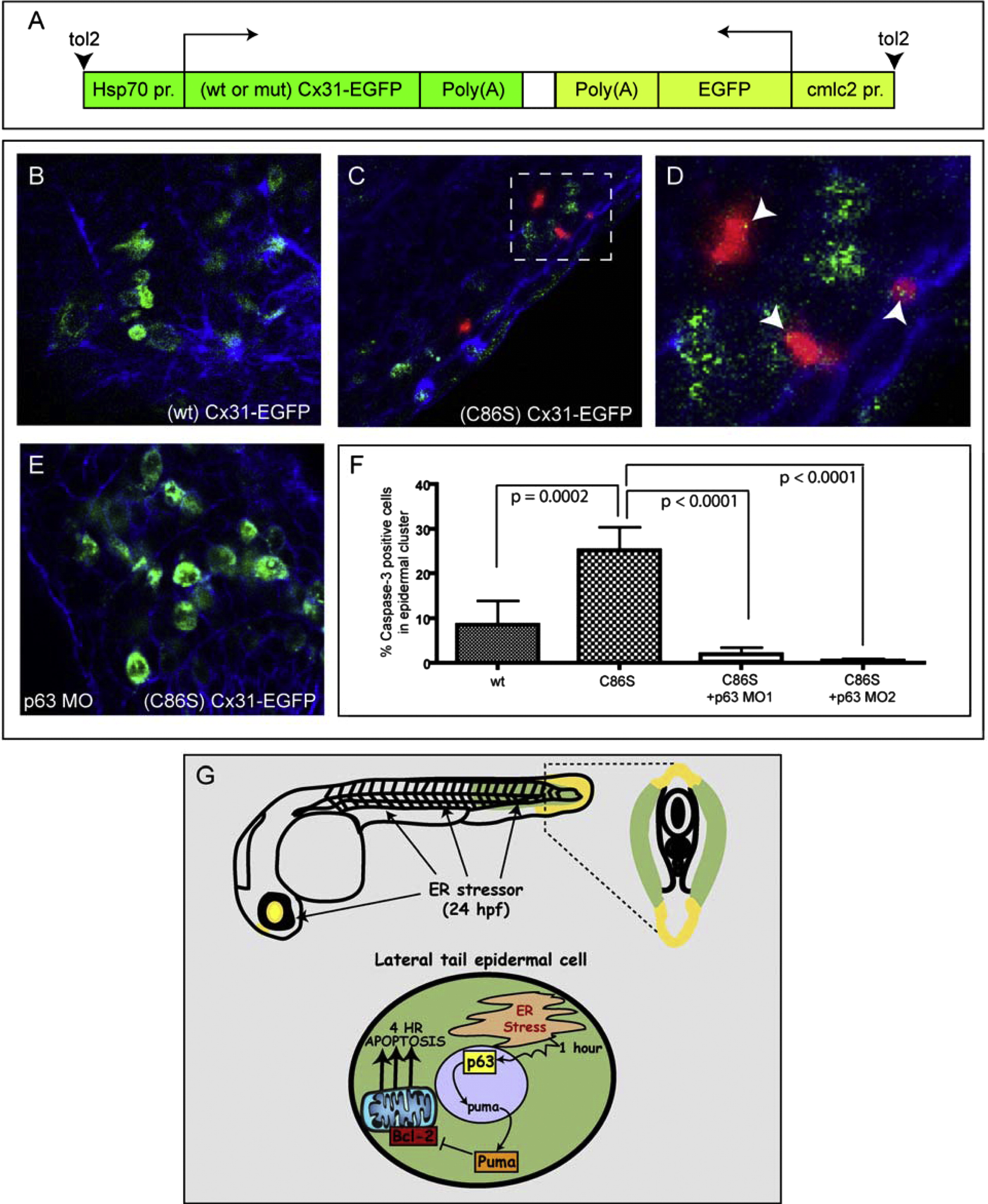
Fig. 7
p63 Is Required for Apoptosis Induced by a Mutant Connexin 31 Construct Associated with Human EKV Disease
(A) Overview of the Cx31 DNA constructs used in this study.
(B–F) p53 mutant embryos were injected with wt or (C86S) mutant Cx31-EGFP constructs, then heat shocked at 24 hpf to induce Cx31-EGFP expression, fixed at 2 hr later, and processed for anti-EGFP (green), anti-activated Caspase-3 (red) and phalloidin staining (blue). See also Figure S6. (B) (wt) Cx31-EGFP caused minimal apoptosis. (C) (C86S) Cx31-EGFP caused a higher level of epidermal apoptosis than (wt) Cx31-EGFP. (D) Zoomed region from (C). (E) Coinjection of p63 MO1 blocked the apoptosis induced by (C86S) Cx31-EGFP. (F) Quantification of apoptosis expressed as % Caspase-3 positive cells in an EGFP positive epidermal cluster. At least eight embryos per condition were used for quantitation.
(G) A model for the mechanism of ER stress-induced apoptosis in the developing epidermis.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 21(3), Pyati, U.J., Gjini, E., Carbonneau, S., Lee, J.S., Guo, F., Jette, C.A., Kelsell, D.P., and Look, A.T., p63 Mediates an Apoptotic Response to Pharmacological and Disease-Related ER Stress in the Developing Epidermis, 492-505, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell