Fig. 3
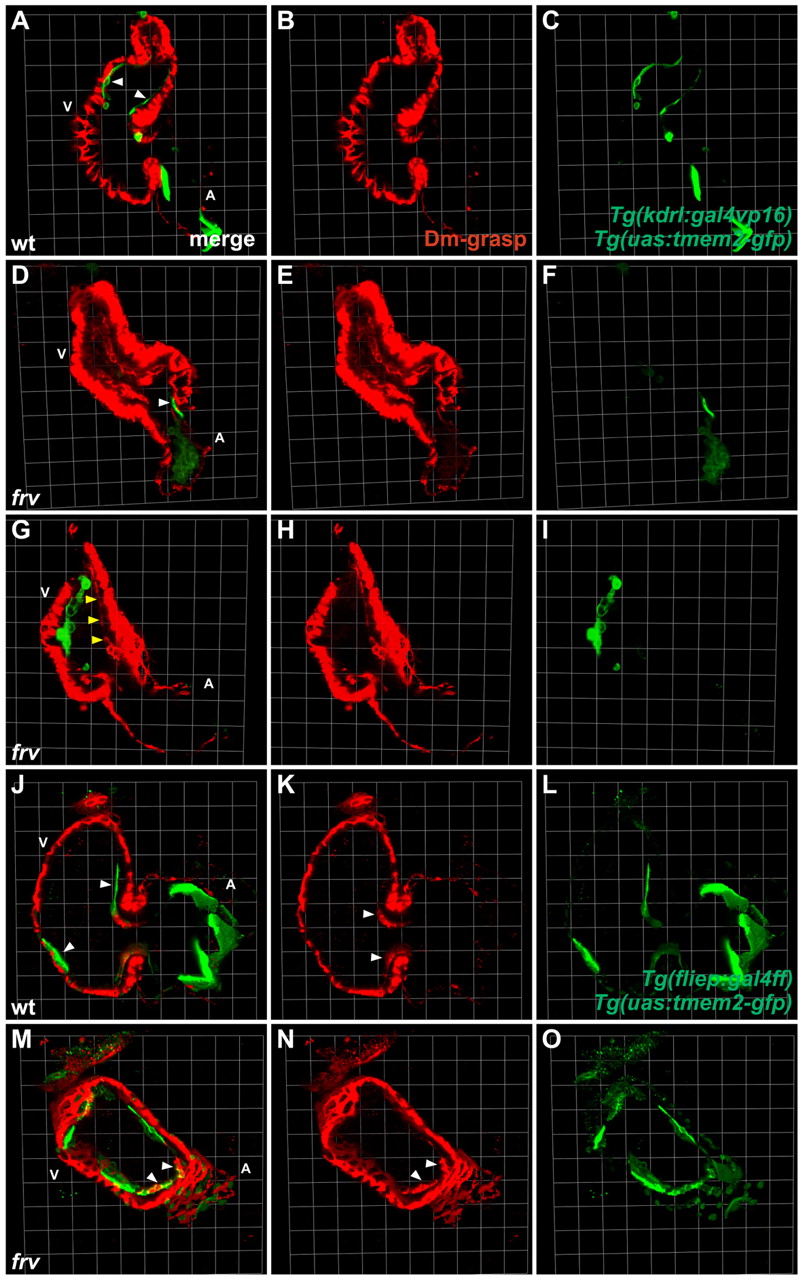
Endocardial expression of tmem2 rescues the frv mutant endocardium. Three-dimensional projections of selected confocal sections of wild-type (A-C,J-L) and frv mutant (D-I,M-O) zebrafish hearts expressing tmem2-gfp (green) in the endocardium at 57 hpf. Immunofluorescence indicates Dm-grasp localization (red). (A-I) Transient mosaic expression of tmem2-gfp is driven by injection of the transgenes Tg(kdrl:gal4vp16) and Tg(uas:tmem2-gfp). (J-O) Mosaic expression of tmem2-gfp is driven by stably integrated Tg(fliep:gal4ff) and Tg(uas:tmem2-gfp) transgenes. (A-C,J-L) Expression of tmem2-gfp in ventricular endocardium (A,J, arrowheads) does not affect wild-type development. (D-F) Ectopic Dm-grasp remains in the frv mutant ventricle when tmem2-gfp is expressed only in atrial endocardium (D, arrowhead). (G-I) Mosaic expression of tmem2-gfp in the ventricular endocardium of frv mutants suppresses ectopic Dm-grasp localization. Ventricular endocardium that does not express tmem2-gfp retains ectopic Dm-grasp (G, arrowheads). (M-O) Broad tmem2-gfp expression in the ventricular endocardium rescues ectopic Dm-grasp expression in an frv mutant. AVC endocardium still expresses Dm-grasp as in wild type (compare M,N with K, arrowheads). Endocardial expression of tmem2-gfp does not improve ventricular contractility, but does reduce the abnormal gap between the myocardium and endocardium. Grids are 23 μm per segment.