Fig. S4
Related to Figure 4. Validation of sflt1-Splice Morpholino (MO), Quantification of the Vascular Effects of Different flt1 Morpholinos, Validation of the GAL4FF Driver Line Tg(fliep:gal4ff)ubs4 and Vascular Effects of the Endothelial-Specific Over-Expression of flt1 Isoforms
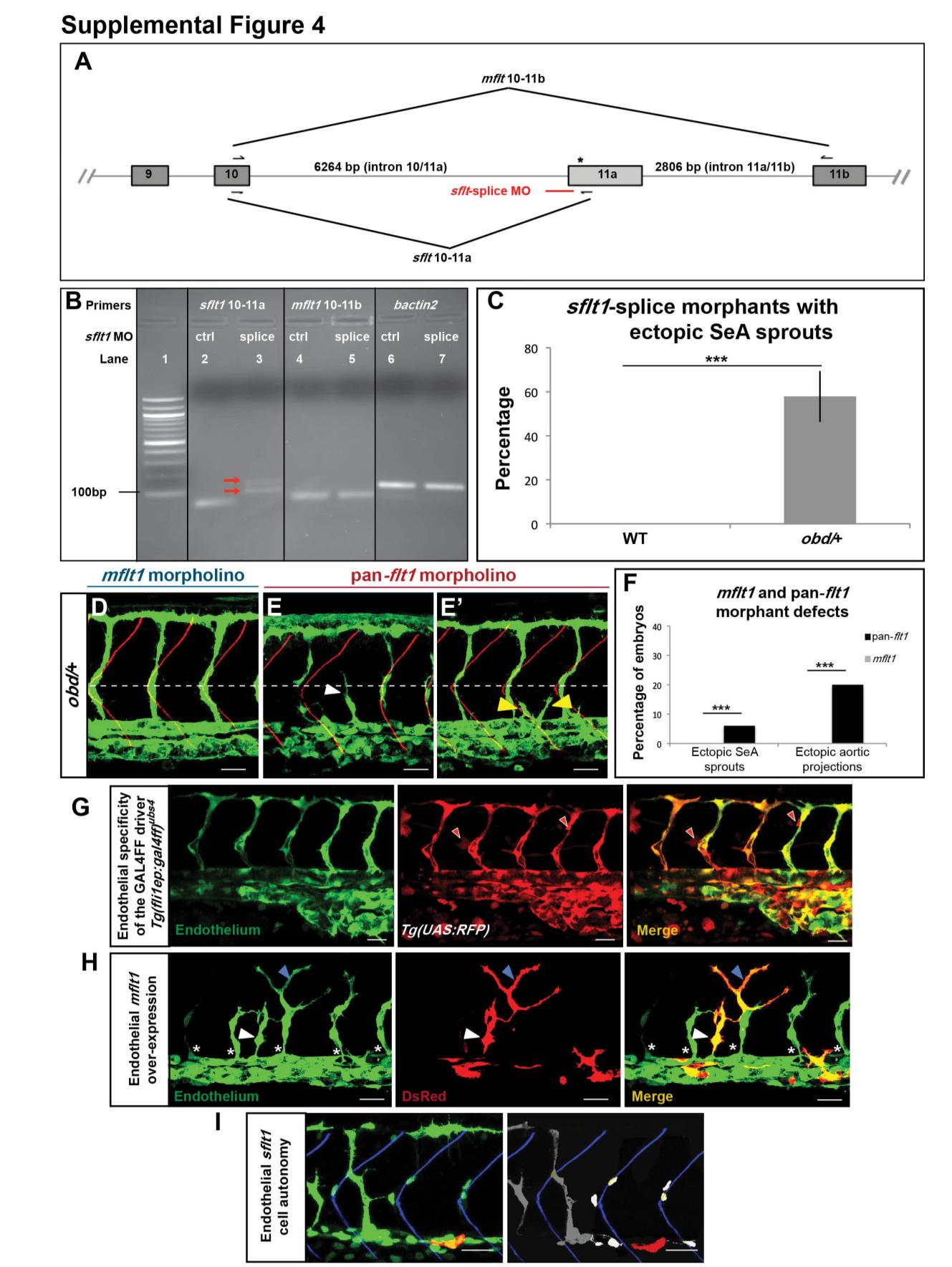
(A) Diagram of flt1′s pre-mRNA (only exons 9-11b shown, not drawn to scale). Exons, boxes. Introns, grey lines. Hemiarrows, mflt1 and sflt1 primers. Red line, sflt1-splice MO. Asterisk, stop codon (exon 11a′s bp 19-21). (B) Validation of the sflt1-splice MO, DNA electrophoresis gel. Lane 1, 100 bp DNA ladder. Lanes 2-7, RT-PCR products obtained from embryos treated with 25 ng of sflt1-ctrl (lanes 2, 4, 6) or sflt1-splice MOs (lanes 3, 5, 7). The correctly spliced sflt1 RT-PCR product (85 bp) seen in sflt1-ctrl morphants (lane 2) is absent from sflt1-splice morphants (lane 3), which show two products larger (red arrows) than those seen in correctly spliced sflt1. Hence, the sflt1-splice MO appears to block the canonical splice site at the intron 10/11a-exon 11a junction, forcing the use of a cryptic splice site (Morcos, 2007). mflt1 and bactin2 are unaffected by either sflt1 MO (lanes 4-7). (C) Percentage of WT (left) and obd/+ (right, grey bar) sflt1-splice morphants with ectopic SeA sprouting. n = 20 WT and n = 19 obd/+. (D-E′) Endothelium, green. Somite boundaries, red. Horizontal myoseptum, white dotted line. White arrowhead, ectopic SeA sprouts. Yellow arrowheads, ectopic aortic projections. Characteristic defects induced by treating obd/+ with 10 ng of mflt1 (D) or previously validated pan-flt1 (E-E′) morpholinos. Scale bars, 50 μm. (F) Quantification of the vascular defects of mflt1 and pan-flt1 obd/+ morphants, including ectopic SeA sprouts (as in E) and ectopic aortic projections (as in E′). n = 30 for both morpholinos. ***p < 0.001. Error bars, s.e.m. (G) Tg(fliep:gal4ff)ubs4 drives endothelial-specific expression of the responder Tg(UAS:RFP) line. 32 hpf trunk vasculature of a Tg(fli:EGFP)y1/+; Tg(fliep:gal4ff)ubs4/+; Tg(UAS:RFP)/+ embryo. Endothelium, green (EGFP). GAL4FF/UAS mediated RFP expression (red). Red filled arrowheads, examples of ectopic, non-endothelial RFP expression. (H) Tg(fliep:gal4ff)ubs4-mediated EC-specific mosaic mFlt1 over-expression can induce ectopic and mispatterned SeA sprouts in WT embryos. 32 hpf trunk vasculature (green) with EC-specific co-expression of mFlt1 and DsRed (red). White arrowheads, ectopic DsRed+ SeA sprout over-expressing mFlt1. Blue arrowheads, misshapen EC over-expressing mFlt1 found within a properly positioned SeA. White asterisks, properly positioned SeA sprouts without mFlt1 over-expression. (I) sflt1 acts cell autonomously within the endothelium. Trunk vasculature (green) of a chimeric 32 hpf embryo made by transplanting obd cells from a Tg(fli:EGFP)y1/+; Tg(fliep:gal4ff)ubs4/+ donor with mosaic, endothelial-specific GAL4FF-dependent co-expression of sflt1 and DsRed (red) into a WT Tg(flk1:EGFP-NLS)/+ host. obd donor ECs (cytosolic green, left) over-expressing sflt1 (DsRed+, red) fail to form SeA sprouts. In contrast, obd ECs not over-expressing sflt1 (cytosolic green, left; grey, right) and WT ECs (nuclear green, left; white, right ? only the nuclei of cells within SeA sprouts are shown) form SeA sprouts even when adjacent to obd ECs over-expressing sflt1 (red). Somite boundaries, blue. (G-I) Scale bars, 30 μm. Anterior, left; dorsal, up.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 21(2), Zygmunt, T., Gay, C.M., Blondelle, J., Singh, M.K., Flaherty, K.M., Means, P.C., Herwig, L., Krudewig, A., Belting, H.G., Affolter, M., Epstein, J.A., and Torres-Vazquez, J., Semaphorin-PlexinD1 Signaling Limits Angiogenic Potential via the VEGF Decoy Receptor sFlt1, 301-314, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell