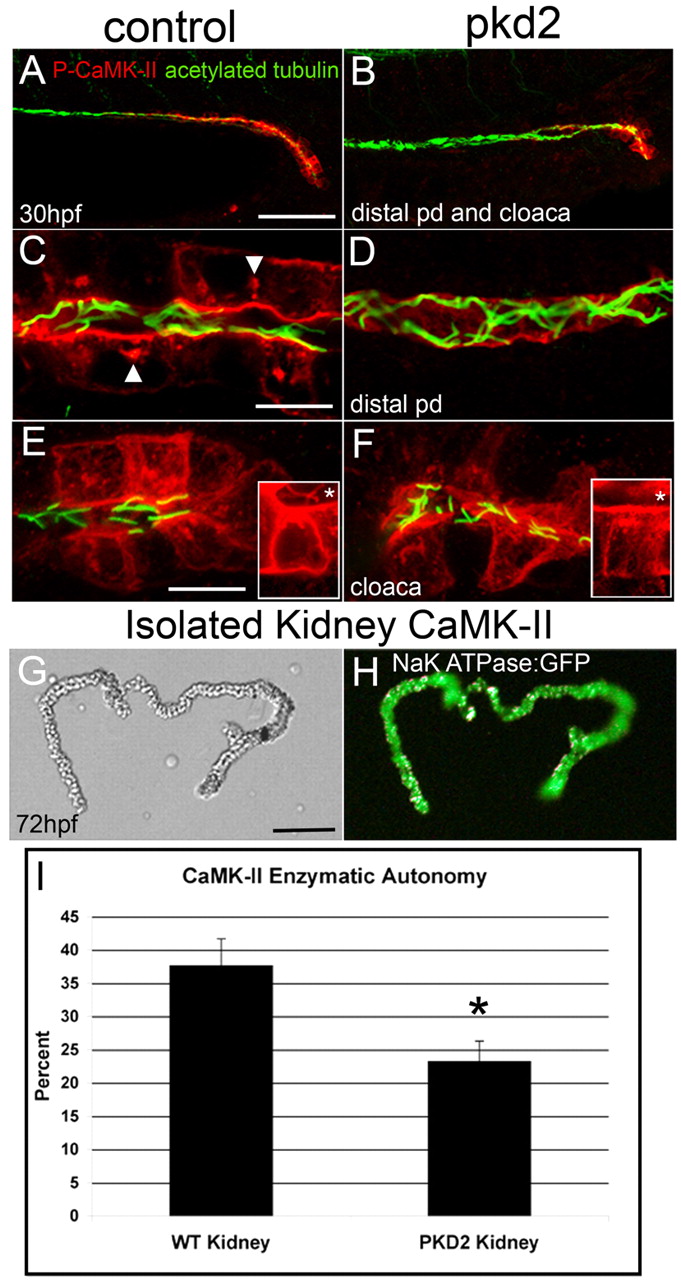
Fig. 8
Active CaMK-II is reduced in pkd2 morphants. (A,C,E) Control and (B,D,F) pkd2 morphants were fixed at 30 hpf and immunolabeled with P-CaMK-II and counterstained for acetylated tubulin. (A,B) P-CaMK-II is reduced in both the distal pronephric duct and cloaca in the morphant. (C) High-magnification image of the distal pronephric duct identifies activated CaMK-II at the apical and basolateral surfaces and in clusters (arrowheads). (D) Activated CaMK-II is lost or greatly diminished in pkd2 morphants. (E,F) P-CaMK-II is reduced, but not absent from cloacal cells in F, but completely lost from cloacal cilia, which are present and normally exhibit activated CaMK-II (inset,*). The insets are z-stack projections of a single cloacal cell stained only with P-CaMK-II. (G,H) Pronephric ducts were dissected from α1 Na+/K+-ATPase-GFP transgenic embryos at 72 hpf. (G) DIC and (H) fluorescence images. (I) CaMK-II enzymatic assay of isolated 3 dpf kidneys shows the reduction, but not elimination of CaMK-II enzymatic autonomy in pkd2 morphants. *P<0.005. Scale bars: 50 μm in A,G; 10 μm in C,E.