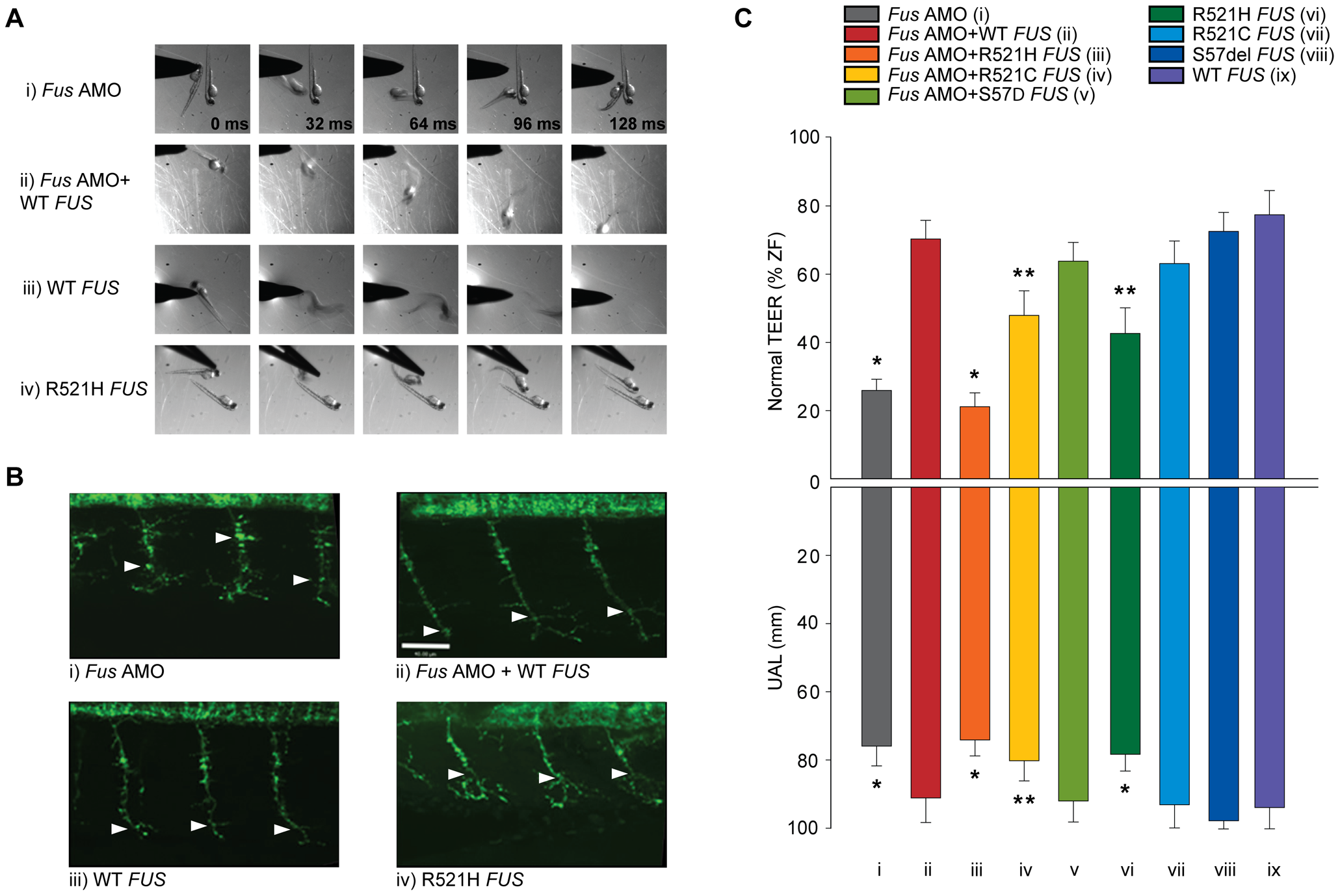
Fig. 2
ALS-related FUS mutations cause a motor phenotype through both gain and loss of function.
A) KD of Fus (i) causes a major deficit in the TEER, which can be rescued by WT FUS mRNA (ii). A similar motor phenotype is also observed upon overexpression of mutant R521H FUS mRNA (iv), but not WT FUS mRNA alone (iii). B) Immunocytochemical analysis of axonal projections from spinal cord motor neurons revealed a marked reduction of primary axonal length (arrowheads represent the unbranched axonal length; UAL) upon KD of zebrafish Fus, which could be rescued by co-expression of WT FUS mRNA (ii). A similar axonal phenotype is also observed upon overexpression of mutant FUS mRNA (iv), but not present in zebrafish expressing WT FUS mRNA (iii) alone. C) Both the percentage of fish with normal TEER (upward bars, averages of % of normal zebrafish (ZF) embryos ▒ standard errors of mean, SEM) and the length of primary motor axons (downward bars, averages of UAL in Ám ▒ SEM) were unaffected or significantly reduced (* for p<0.05 from WT FUS mRNA injections; ** for p<0.05 from WT FUS mRNA injections and Fus AMO; all values given in Table 1) when compared to fish injected with Fus AMO alone (i), Fus AMO and WT FUS (ii), Fus AMO and R521H FUS (iii), Fus AMO and R521C FUS (iv) and Fus AMO and S57Δ FUS (v), or with R521H FUS (vi), R521C FUS (vii), S57Δ FUS (viii) or with WT FUS mRNA alone (ix). Arrowheads represent length to the first axonal branching (UAL). Scale bar: 40 μm.