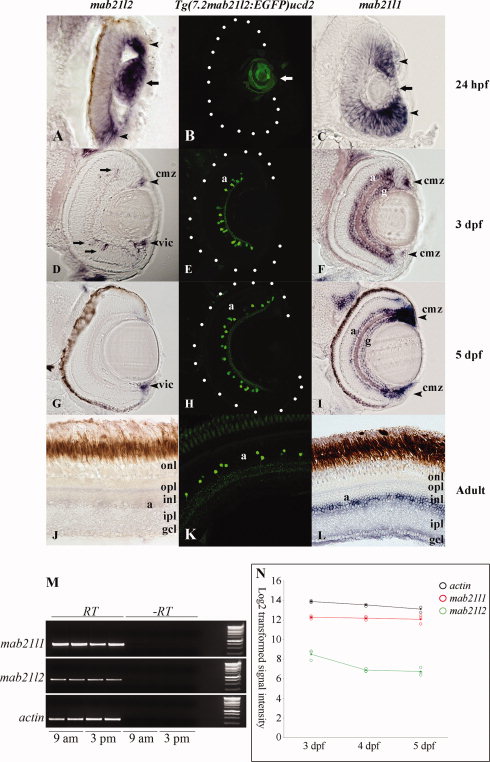
Fig. 4
Comparison of the ocular expression of mab21l1, mab21l2, and Tg(7.2mab2ll2:EGFP)ucd2. In <24 hpf eye sections, Tg(7.2mab2ll2:EGFP)ucd2 expresses EGFP in the lens (B), partly recapitulating mab21l2 (A), but not mab21l1, which is widely expressed in the retina (C). At 3 dpf, mab21l2 is weakly expressed in the peripheral INL, dorsal ciliary marginal zone, and ventral iridocorneal canal (D), whereas mab21l1 is upregulated in amacrine and ganglion cell layers (F). From 3 dpf to adult, Tg(7.2mab2ll2:EGFP) is expressed in a subpopulation of amacrine cells in the INL (E,H,K) and thereby partly recapitulates a prominent expression domain of mab21l1 (I,L). In contrast, mab21l2 is only expressed in the ventral iridocorneal canal at <5 dpf (G) and is undetectable in adult sections (J). mab21l1 and mab21l2 expression levels assayed by RT-PCR of 5-dpf eyes. At 5 dpf, mab21l1 is expressed at higher levels than mab21l2. Duplicate RNA samples were isolated at 9 am and 3 pm to confirm that transcription levels did not change during the day. Actin was used as a control (M). mab21l1 and mab21l2 expression levels assayed by microarray analysis of 3?5-dpf eyes This confirmed higher expression levels in the eye of mab21l1 in relation to mab21l2at 3?5 dpf, with decreasing mab21l2 transcript levels after 3 dpf (N). Arrow (A,C), lens; arrowhead (A,C), mab21l1/mab21l2 expression domains; Arrows (D), mab21l2-expressing cells; a, amacrine cell layer; g, ganglion cell layer; cmz, ciliary marginal zone; vic, iridocorneal canal; opl, outer plexiform layer; onl, outer nuclear layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; ipl, inner plexiform layer; gcl, ganglion cell layer.