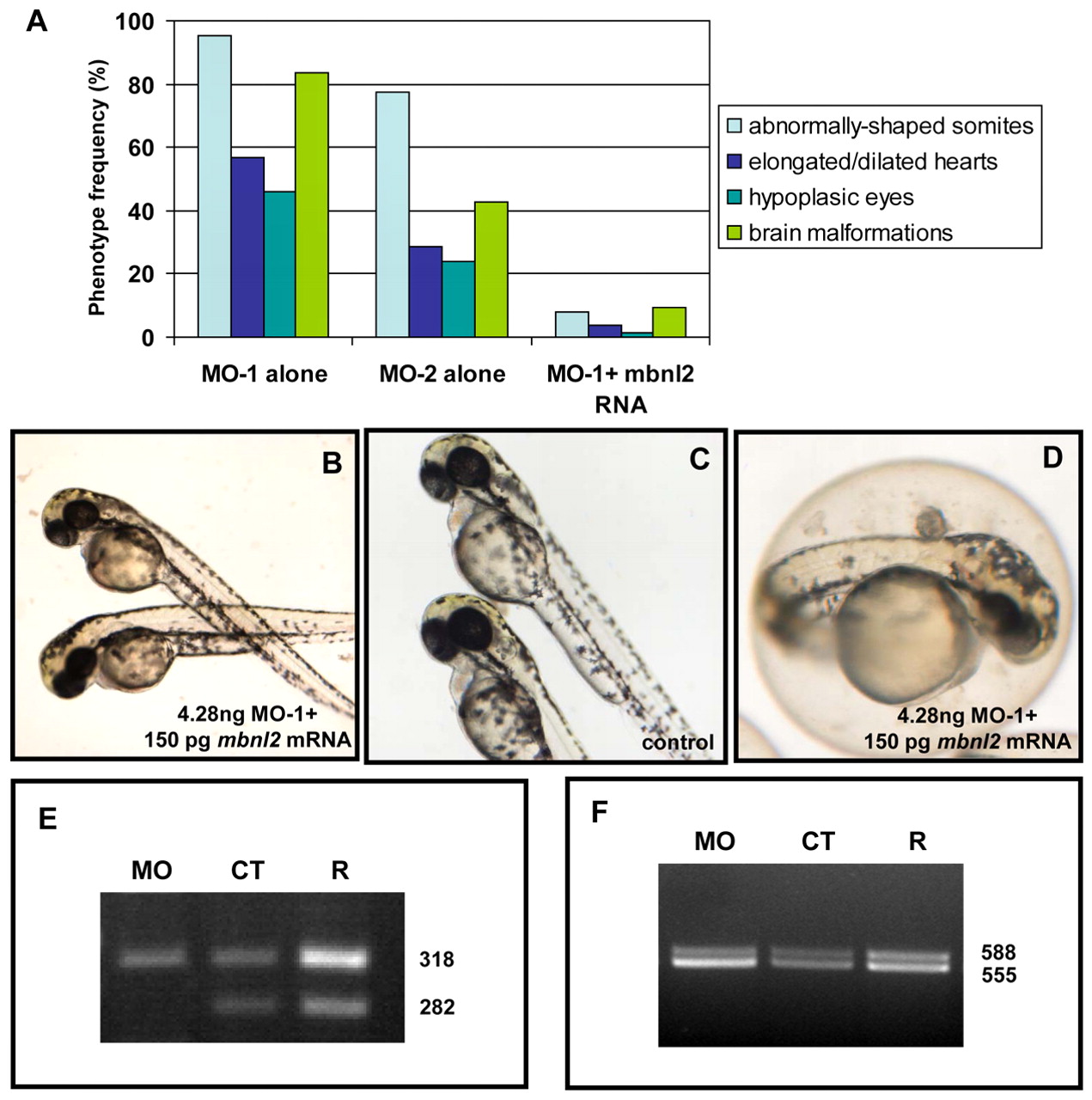
Fig. 5
The mbnl2 morphant phenotype can be rescued by mbnl2 and MBNL2 mRNAs, in a dose-dependent manner. (A) The phenotype induced by MO-1 is rescued by co-injection with mbnl2 mRNA. The histogram shows the frequency of the observed phenotype after injection of 4.28 ng MO-1 or the same amount of MO-2 (n=100, from five independent experiments). The percentage of affected embryos is significantly reduced when 150 pg mbnl2 mRNA is co-injected with 4.28 ng MO-1. (B,C) The completely rescued embryos (B) are indistinguishable from the controls (C). (D) The partially rescued embryos show a mild phenotype consisting of the presence of slight eye pigmentation defects, minor heart hypoplasia, mild spinal defects, and a head that is protuberant at the fourth ventricle level of the hindbrain. (E,F) The normal splicing pattern of tnnt2 (E) and clcn1 (F) is restored by co-injection of MO-1 with mbnl2 mRNA. The ratio of the upper and lower band is 1:2 in the morphants (MO), whereas, in controls (CT), it is 1:1.46, and is 1:1.34 in the rescued embryos (R). When co-injecting the human homologue, 75 pg of MBNL2 mRNA is the most effective dose in compensating the phenotype induced by MO-1 (Table 2).