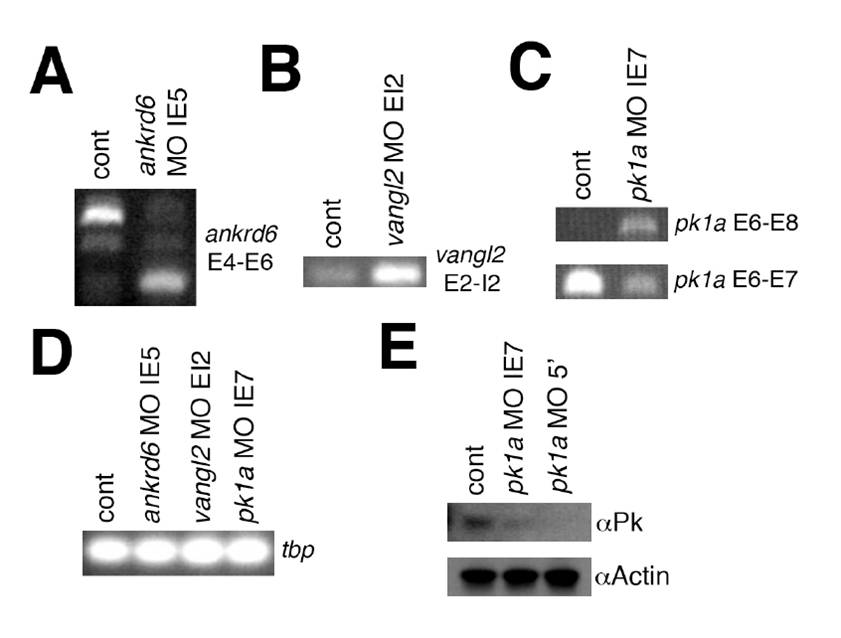
Fig. S1 Documentation of morpholino knockdown. (A-D) PCR of 24 hpf embryos injected at the 1-cell stage with control and (A) ankrd6 morpholino (MO), (B) vangl2 MO, (C) pk1a MO, and each of the above (D), at the amounts used to elicit the phenotypes noted elsewhere (1.5 ng). (A) There is loss of a 375 bp ankrd6 PCR product spanning exon 4 and exon 6 (E4-E6) in embryos injected with an ankrd6 MO designed to inhibit splicing into exon 5. The lower part of the panel shows a 125 bp band using the same primers in the same embryos that results from loss of the ~250 bp exon 5. (B) A 202 bp vangl2 PCR product spanning exon 2 (E2) and the intron between exons 2 and 3 (I2) in embryos injected with a vangl2 MO designed to inhibit splicing out of I2, which introduces an in-frame stop codon from sequence within the second intron. (C) A novel 650 bp PCR product spanning pk1a exons 6 and 8 in embryos injected with pk1a MO designed to inhibit splicing into exon 7, as well as a decrease in a 200 bp PCR product spanning E6 and E7 in the same embryos. (D) Apparently similar amounts of a 100 bp tbp PCR product in embryos from each of the above knockdowns. The above results were confirmed using real-time quantitative PCR normalized against hprt or cp (ceruloplasmin). (E) Western blot analysis of 3 dpf larvae injected at 2 dpf with control (cont) or pk1a MOs. The upper panel shows a decrease in the 70 kDa Prickle band using anti-Prickle (αPk) antibody, while the lower shows constant Actin expression using αActin antibody.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 351(2), Cui, S., Capecci, L.M., and Matthews, R.P., Disruption of planar cell polarity activity leads to developmental biliary defects, 229-241, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.