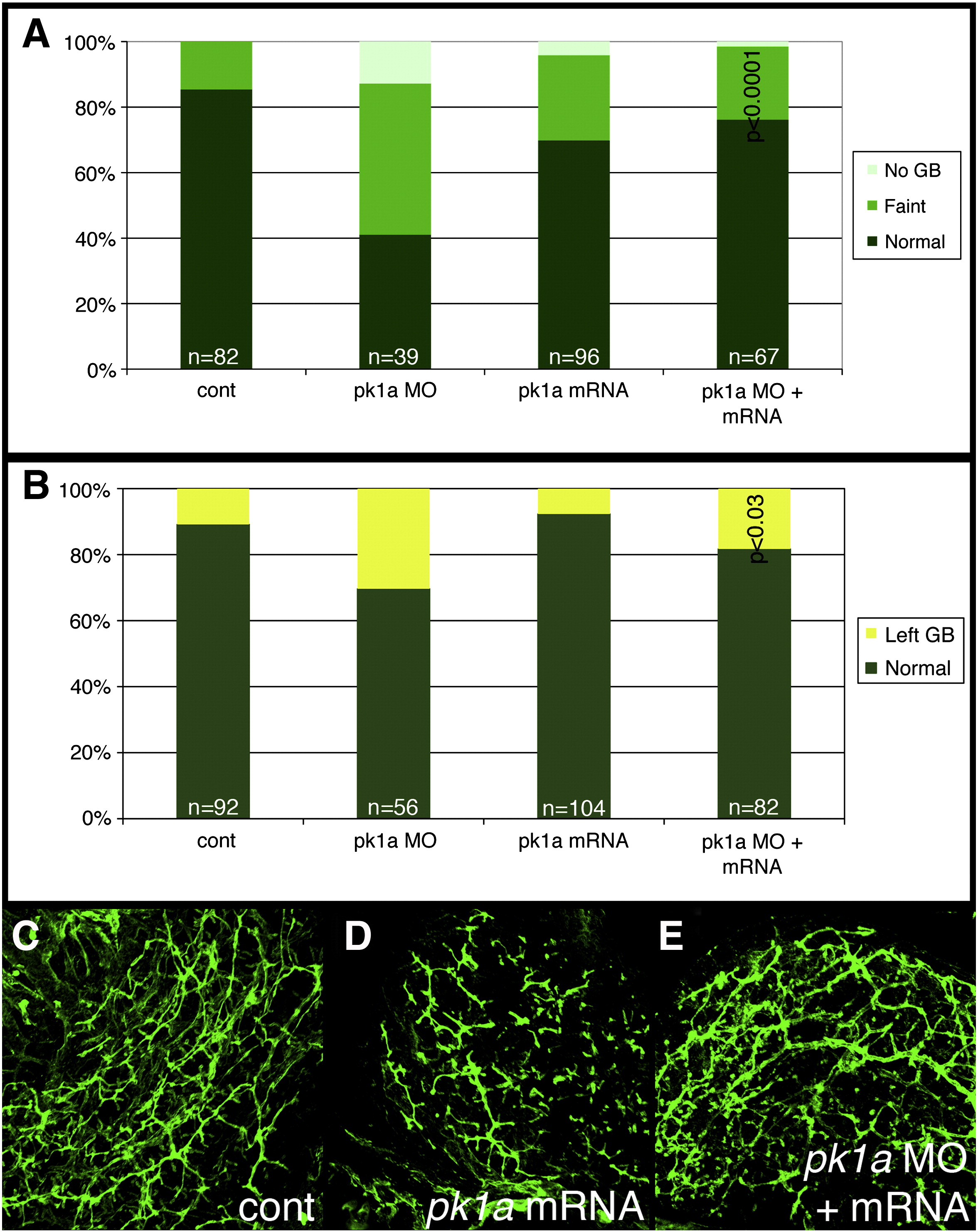
Fig. 4 Effect of pk1a on biliary development. (A, B) Bar graphs depicting PED6 uptake in control (cont), pk1a morpholino-injected (pk1a MO), pk1a mRNA-injected, and pk1a MO and mRNA-injected larvae. In (A), the percentage of larvae with no gallbladder (GB) uptake, faint uptake, and normal uptake is depicted on the Y-axis. In (B), numbers of larvae with abnormal left-sided GBs are depicted. Note that pk1a mRNA injection leads to an increase in the number of faint gallbladders compared to control (p < 0.0001), while mRNA injection leads to a rescue of the MO phenotype (p < 0.0001 compared to MO injection, NS compared to control). Forced expression of pk1a mRNA has no effect on GB sidedness, but does rescue the morphant sidedness phenotype. (C?E) Confocal projections of whole-mount cytokeratin staining of livers from 5 dpf control (B, cont), pk1a mRNA-injected (C) and pk1a MO and mRNA injection (D). Note that mRNA injection alone leads to scattered short duct-like structures, while mRNA and MO co-injection leads to rescue of the MO phenotype.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 351(2), Cui, S., Capecci, L.M., and Matthews, R.P., Disruption of planar cell polarity activity leads to developmental biliary defects, 229-241, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.