Fig. 5
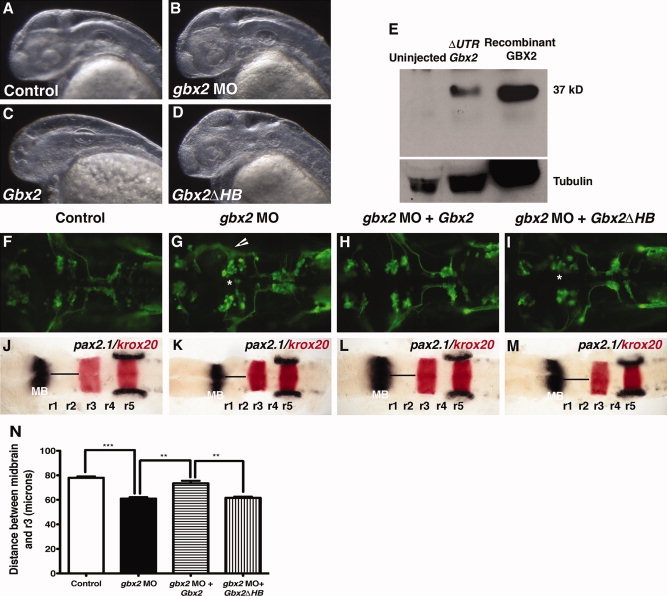
Mouse GBX2 functions in Zebrafish. Overexpression of mouse Gbx2 mRNA affects the formation of the forebrain in zebrafish embryos. A?D: Lateral view at 36 hpf, anterior to the left of embryos viewed by darkfield microscopy. A,B,D: Control embryo (A) and embryos injected with 8 ng gbx2-MO (B) or 120 pg of truncated mouse Gbx2 mRNA (D) do not show morphological defects in the forebrain. C: Partial or complete truncation of the forebrain was observed in embryos injected with complete mouse Gbx2 coding sequence. E: Western blot of total lysates from 10-hpf embryos showing expression of mouse GBX2 protein translated from complete ΔUTRGbx2. Recombinant mouse GBX2 protein expressed in E. coli, was used as a positive control. Expression of mouse GBX2 rescues anterior hindbrain defects caused by gbx2-MO. F?M: Dorsal views anterior to the left of Tg(isl1:gfp) embryos. F?I: The expression of GFP at 36 hpf. Abnormal cell body clustering was observed in embryos injected with gbx2-MO (B). J?M: Whole-mount in situ hybridization examining the expression of pax2.1 (black) and krox20 (red) at 20-somite stage. K: Injection of gbx2-MO results in truncation between the midbrain and r3. Embryos co-injected with gbx2-MO/Gbx2 mRNAs show complete rescue of abnormal nV cell body clustering (H) and anterior hindbrain truncation (L). Co-injection with gbx2-MO/Gbx2ΔHB mRNAs does not rescue anterior hindbrain defects (I,M). N: Distance between posterior midbrain and r3. Arrows indicate disruption of distinct nV clustering in r2 and r3. *, Abnormal nV cell body clustering. **P < 0.001 (Student′s t-test), ***P < 0.0001 (Student′s t-test); arrowheads, ectopic axonal branching; hpf, hours post fertilization; HB, homeobox; MB, midbrain; MO, morpholino; r, rhombomere.