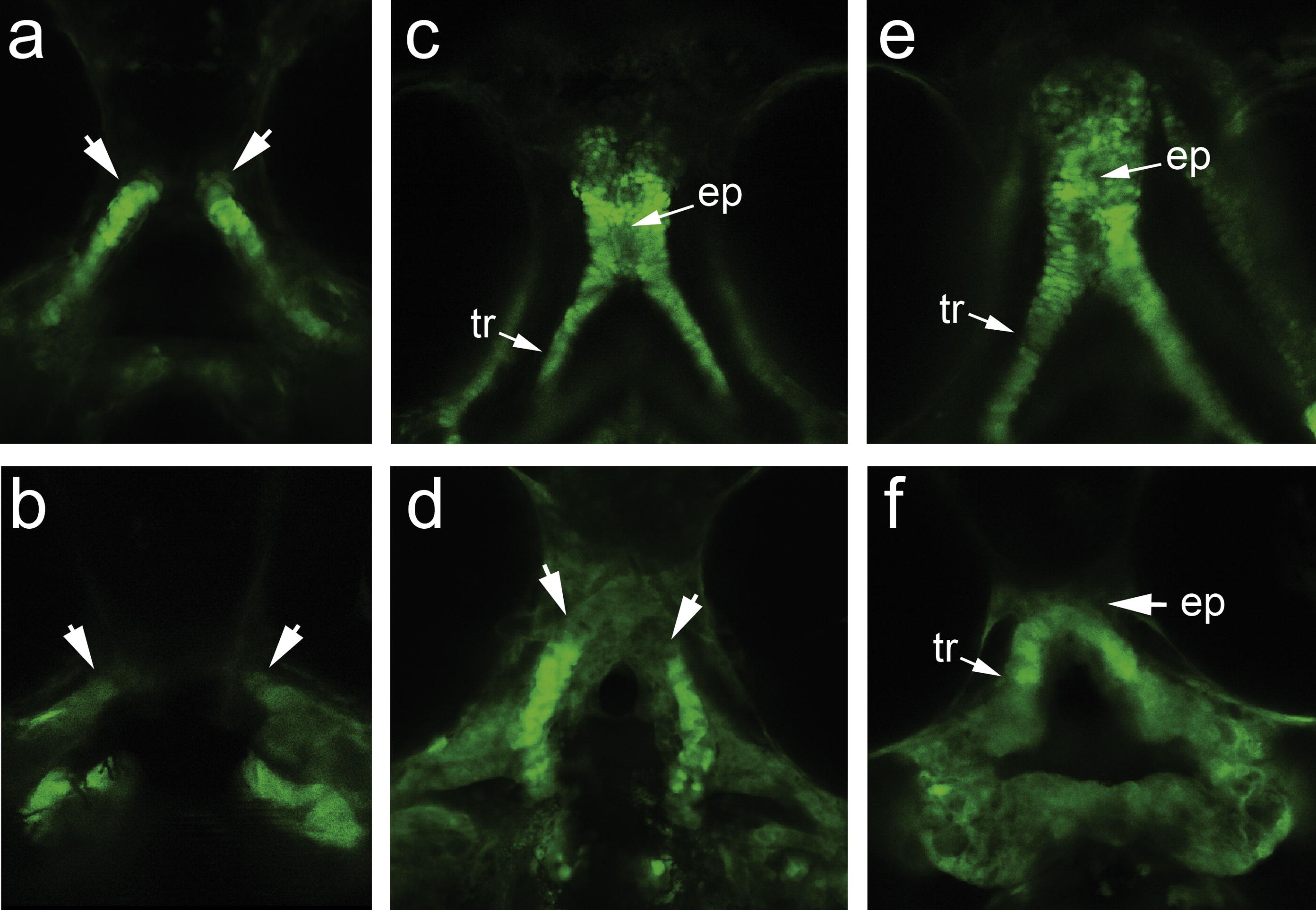
Fig. 5 Analysis of cranial neural crest cells after wnt9a knockdown in sox10:eGFP transgenics. Embryos injected with MM control (a, c and e) and translation-blocking MO (b, d and f), where the cranial neural crest cells (CNCC) are followed over embryogenesis. Embryos are shown in ventral views at 48 hpf (a and b), 72 hpf (c and d) and 96 hpf (e and f). Initial CNCC delamination from the neural plate occurs normally in the MO injected embryos (not shown) and the first distinct phenotype is observed with when the dorsal group of CNCC that differentiate into the trabeculae become obliquely oriented and the distal leading edge migrate toward the midline (arrows, a). In the MO injected embryos, the dorsal CNCC fail to move medially, resulting in a wide separation between the CNCC groups. At 72 hpf, the ethmoid plate and the trabeculae are formed (c). In the morphant, the trabeculae is formed but does not join in the midline, and the ethmoid plate is absent (d). By 96 hpf, the distal edges of the morphant trabeculae come into the midline and is joined by 1–2 cell layers of tissue, with absent ethmoid plate (f). Abbreviations: ep (ethmoid plate), tr (trabeculae).
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 128(1-2), Curtin, E., Hickey, G., Kamel, G., Davidson, A.J., and Liao, E.C., Zebrafish wnt9a is expressed in pharyngeal ectoderm and is required for palate and lower jaw development, 104-115, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.