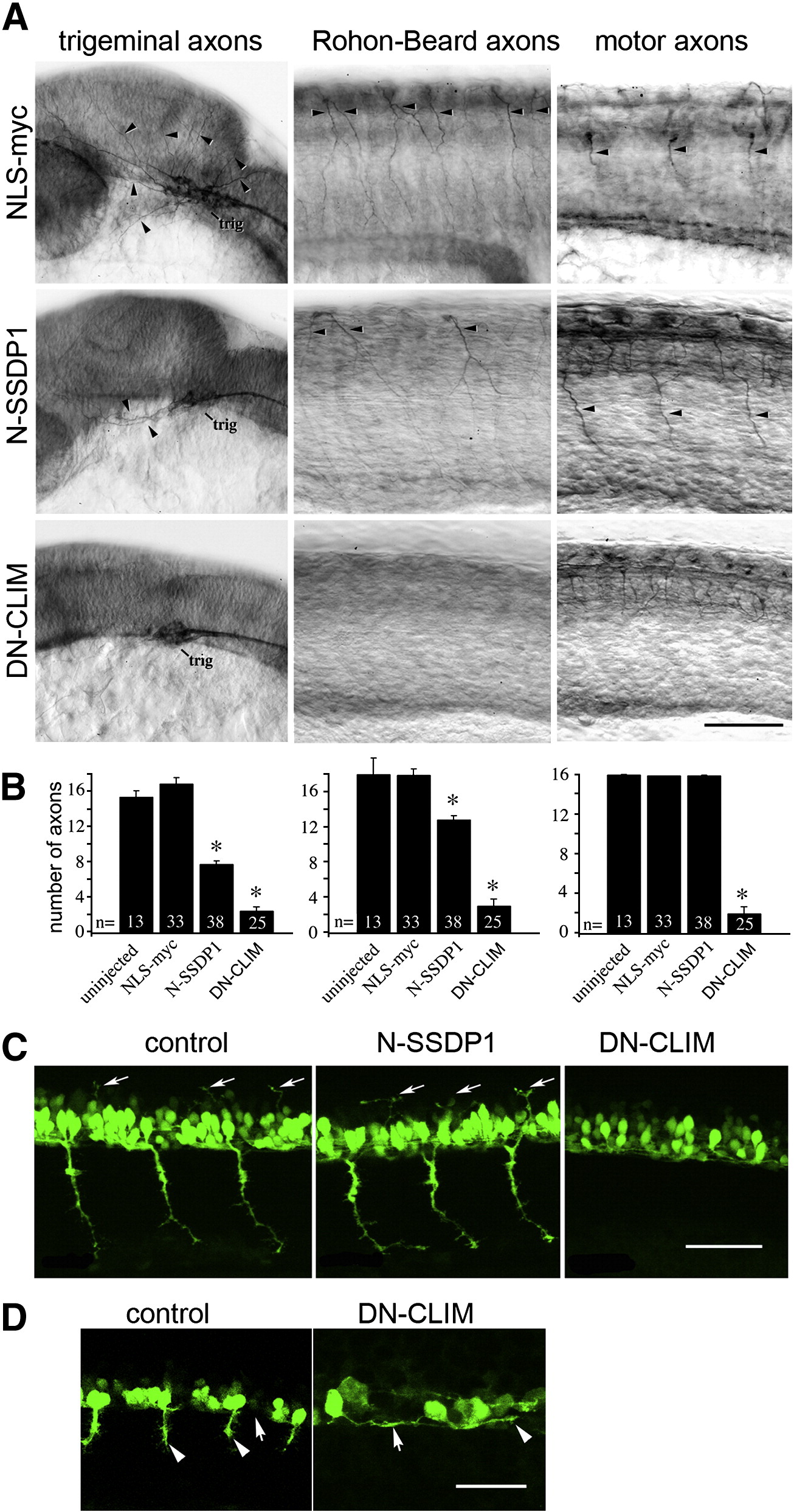
Fig. 5 Phenotypes induced by N-SSDP over-expression partially overlap with those induced by DN-CLIM over-expression. A: Lateral views of anti-tubulin immuno-labeled whole-mounted 24 hpf embryos are shown. Injection of N-SSDP1 mRNA leads to loss of peripheral axons of trigeminal (trig) and Rohon?Beard neurons, but not of ventral motor axons (NLS-myc = control mRNA). DN-CLIM mRNA injections affect all three types of axons. Arrows indicate axons. B: Quantification confirms significant loss of peripheral sensory but not motor axons upon N-SSDP1 over-expression, whereas DN-CLIM over-expression affects also motor axons. C: DN-CLIM, but not N-SSDP1 over-expression inhibits growth of dorsal MiP axons (arrows), as shown in lateral trunk views of HB9:GFP transgenic embryos at 28 hpf. D: Higher magnification of the ventral border of the caudal spinal cord (arrows) at 24 hpf shows that HB9:GFP+ motor neurons grow axons (arrowheads) ventrally out of the spinal cord in controls. In DN-CLIM mRNA injected embryos axons grow along the ventral border of the spinal cord. Scale bars = 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 349(2), Zhong, Z., Ma, H., Taniguchi-Ishigaki, N., Nagarajan, L., Becker, C.G., Bach, I., and Becker, T., SSDP cofactors regulate neural patterning and differentiation of specific axonal projections, 213-224, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.