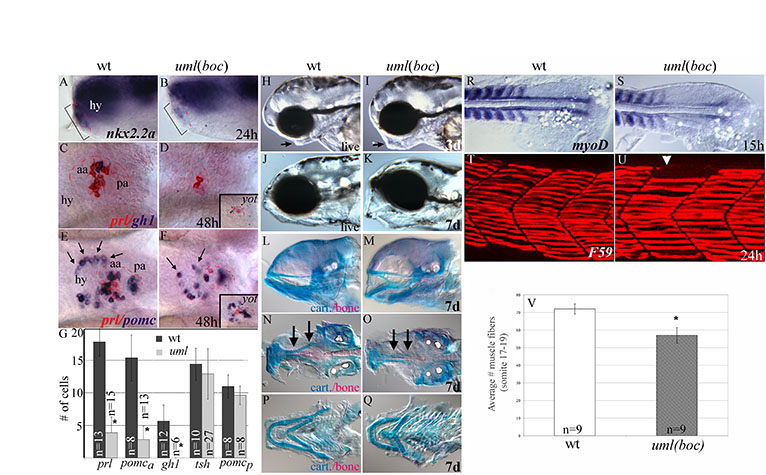
Fig. S2
Fig. S2 Pituitary, jaw and muscle defects in uml(boc) mutants. (A,B) Lateral views of the anterior/ventral forebrain at 24 hpf. (A) The Hh target gene nkx2.2a is expressed in epidermal cells that form the pituitary placode (bracket, red dashes show border with the hypothalamus). (B) In uml mutants, nkx2.2a expression is reduced in the forming placode (bracket, B). (C-F) Ventral views of the forebrain at 48 hpf. (C) prolactin (prl) (red) and growth hormone (gh1) (purple) expressing cells in wild type. (D) uml mutants have no gh expressing cells and severely reduced prl cell numbers, similar to yot(gli2DR) (inset). (E) pomc expression in the hypothalamus (arrows) and anterior (aa) and posterior (pa) halves of the adenohypophysis in wild type. (F) In uml mutants, pomc cells in the hypothalamus are disorganized (arrows) and pomc cell numbers are reduced in the anterior half of the pituitary placode. pomc expression in the posterior half of the adenohypophysis is relatively unchanged. Again, this is similar to the yot Hh pathway mutant (inset F). (G) Average endocrine cell numbers in the adenohypophysis of uml mutants and wild-type individuals showing a significant reduction in prl, anterior pomc (pomca) and gh cells, but not tsh or posterior pomc (pomcp) expressing cells. *P<0.0001. (H-K) Lateral views of the head at 3 and 7 dpf. (H,I) The lower jaw (arrow) is visibly larger at 3 dpf in uml mutants (I) than in wild type (H). (J,K) By 7 dpf the lower jaw is expanded ventrally in uml mutants (K) relative to wild type (J). (L-Q) Alcian Blue staining of cartilage elements and Alizarin Red staining of bone. (L,M) Cartilage elements are expanded ventrally and the jaw is often in an open position in uml mutants (M) relative to wild type (L). (N,O) Ventral views of dissected upper jaws. In uml mutants (O), the cranial bone (red) is thinner relative to wild type (N) and the trabeculae (arrows) are fused at the midline. (P,Q) Ventral views of dissected lower jaws. In uml mutants (Q), cartilage elements (arches) appear slightly thicker and the lower jaw is wider than in wild type (P). This is in contrast to the reduced lower jaw seen in other Hh pathway mutants (Brand et al., 1996). (R,S) Dorsal views of the posterior trunk at 15 hpf. (R) In wild-type embryos, myoD is expressed in newly formed somites and slow muscle precursor (adaxial) cells adjacent to the notochord. (S) uml(boc) mutants have reduced myoD expression in adaxial cells. (T,U) Lateral views of somites 17-19 at 24 hpf. (T) The F59 antibody labeling of slow muscle fibers in wild type. (U) Some slow muscle fibers are absent in some but not all segments of uml(boc) mutants (arrowhead). (V) uml mutants have significantly fewer slow muscle fibers in the trunk (P< 0.0001). Wild-type embryos have an average of 72 slow fibers in somites 17-19 whereas uml(boc) mutants have an average of 57 fibers in these segments. aa, anterior adenohypophysis; cart, cartilage; hy, hypothalamus; pa, posterior adenohypophysis.