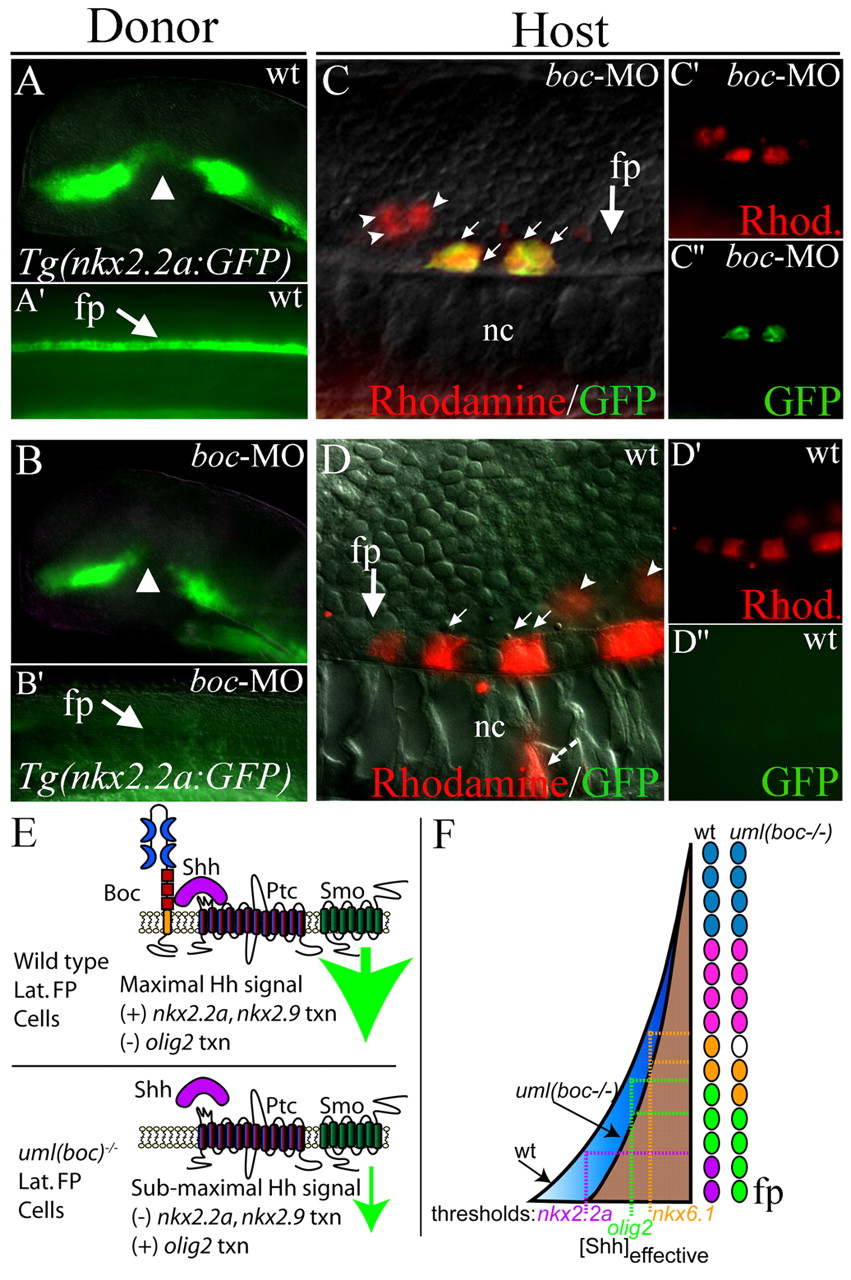
Fig. 6 boc is required cell-autonomously for Hh target gene expression in the ventral spinal cord. (A,A′) GFP expression in a Tg(nkx2.2a:megfp) transgenic donor embryo reports wild-type nkx2.2a expression in the forebrain (A) and spinal cord (A′, lateral view of trunk). (B,B′) Loss of Boc function (boc MO injection) leads to the regional loss of nkx2.2a expression in the forebrain (arrowhead in B) and complete loss of nkx2.2a expression in the floor plate (arrow in B′) in 100% of injected embryos (see Fig. 4). (C-C′) Example of transplanted wild-type cells (Rhodamine; red) in a host embryo that lacks Boc function (boc MO-injected). Wild-type donor cells that are located in the floor plate region (arrows) express nkx2.2a despite the lack of boc function in surrounding cells. More dorsally located cells do not express the nkx2.2a:megfp transgene (arrowheads). nkx2.2a expression was seen in 23 cells in four embryos in this experimental paradigm. For clarity, C′ and C′ show Rhodamine and GFP fluorescence alone. (D) A wild-type host embryo containing cells that lack boc function (from boc MO-injected donors as seen in B). In this scenario, no cells were found that expressed the nkx2.2a:megfp transgene, even when transplanted cells were located in the floor plate region. A total of 59 cells in the floor plate region of six embryos were assayed in this experimental paradigm. For clarity, D′ and D′ show Rhodamine and GFP staining alone. (E) Schematic model of Hh signal levels in wild-type or Boc deficient cells. Boc binding to Shh could facilitate the binding of Shh to Ptc, increasing local concentrations of Shh or the length of binding time, thus generating a maximal Hh signal (large green arrow). Without Boc, the Hh signal is reduced (small green arrow). (F) Schematic model of spinal cord Hh signaling levels in the presence (blue) or absence (brown) of Boc function. Colored circles depict individual cells in the zebrafish spinal cord. Loss of Boc function might lower the effective concentration of Shh in the ventral spinal cord, eliminating expression of genes that require the highest levels of Hh signaling for transcriptional activation (e.g. nkx2.2a). Expression domains for genes with slightly lower Shh thresholds are shifted ventrally. fp, floor plate; nc, notochord.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development