Fig. 3
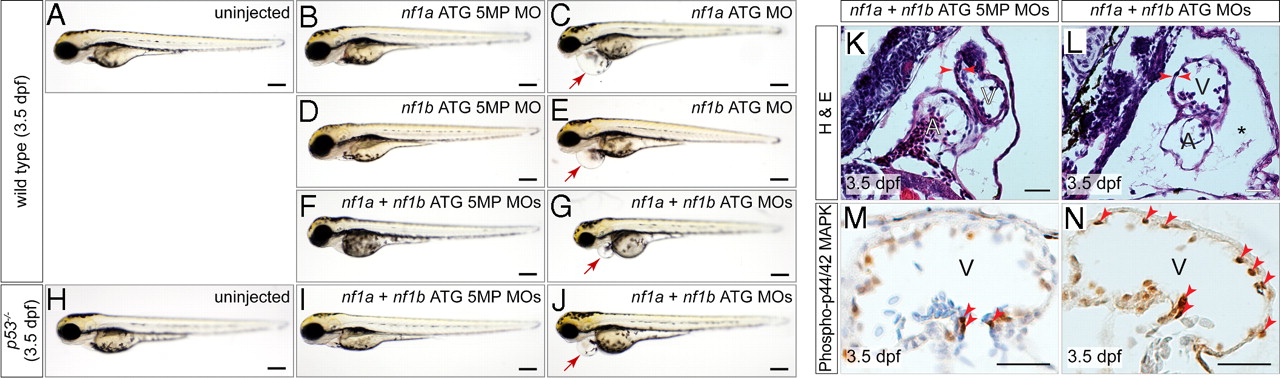
MO knockdown of nf1a, nf1b, or both together results in pericardial effusions at 3.5 dpf and increased phospho-p44/42 MAPK in cardiac tissue. Analysis of 3.5-dpf wild-type embryos (A) or embryos injected with nf1a ATG 5-mispair (5MP) MO (B), nf1b ATG 5MP MO (D), or nf1a + nf1b ATG 5MP MO (F) reveal no apparent defects in gross morphology. Treatment with nf1a ATG MO (C), nf1b ATG MO (E), or a combination of both (G), however, results in a dilation of the pericardial space. (H?J) Injection of p53-/- embryos with nf1a + nf1b ATG MO results in a gross dilation of the pericardial space (J), whereas uninjected (H) and nf1a + nf1b ATG 5MP MO-injected p53-/- embryos (I) appear normal. (Scale bars: 0.25 mm.) (K and L) Transverse sections of 3.5-dpf nf1a/nf1b combined morphant embryos reveals a thinning of the ventricular myocardium and pericardial effusion (*) when compared with controls (A, atrium; V, ventricle). (M and N) Immunohistochemical analysis of transverse sections of 3.5-dpf nf1a/nf1b combined morphant embryos reveals an increase in the ratio of phospho-p44/42 MAPK-positive cardiac cells (arrows) to the total number of cardiac cells when compared with controls. (Scale bars: 25 μm.)