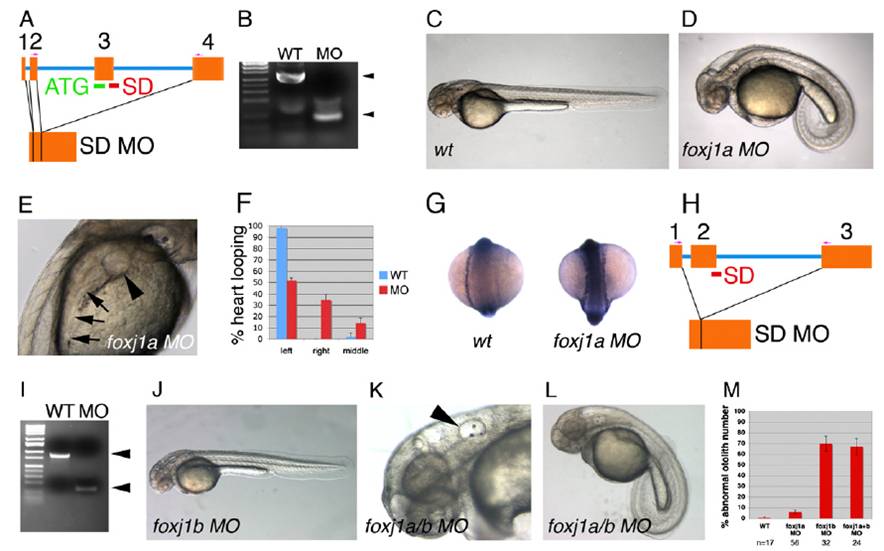
Fig. S5 foxj1a and foxj1b morphants exhibit distinct ciliopathy phenotypes. (A) Genomic structure of the zebrafish foxj1a gene and sites of ATG and splice donor (SD) MO used in this study. SD MO results in complete deletion of exon 3 as determined by sequencing. (B) RT-PCR analysis of control (WT) and foxj1a SD morphant embryo RNA, indicating complete loss of normal foxj1a mRNA induced by mis-splicing in foxj1a SD morphants. (C) Control morpholino-injected zebrafish at 48 hpf compared with (D) zebrafish injected with a mixture of both foxj1a ATG and SD MO, which uniformly exhibited ventrally curved body axis, hydrocephalus, and normal otolith number (two per otic placode), as well as (E) glomerular cysts (arrowhead) and dilated pronephric tubules (arrows). foxj1a morphants showed frequent situs inversus, as determined by assessment of heart-looping (F; error bars represent SD of three averaged experiments; n = 98 embryos total) and bilateral expression of southpaw (G). (H) Intron-exon boundaries for zebrafish foxj1b and the exon 2 SD MO target site. RT-PCR demonstrated complete loss of WT mRNA and deletion of exon 2 in foxj1b morphants (I). (J) foxj1b Morphants appeared relatively normal, with the exception of abnormal otolith number (K; arrowhead depicting otic placode with three otoliths present). (L) foxj1a/b double knockdown embryos demonstrate curved body axis, kidney cysts, hydrocephalus, and abnormal otolith number. (M) Quantification of abnormal otolith number in foxj1a, foxj1b, and foxj1a+b double morphants. Error bars represent standard deviation of three averaged experiments).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA