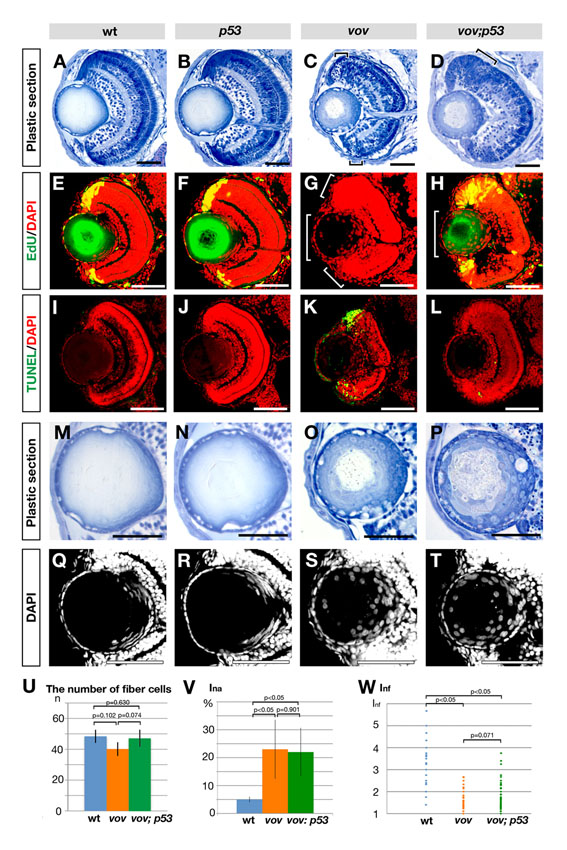
Fig. S6 Retinal and lens phenotypes of zebrafish vov; p53 double mutant. (A-D) Plastic sections of wild-type (A), p53 (B), vov (C) and vov; p53 double mutant (D) eyes at 72 hpf. Apoptosis near the CMZ in the vov mutant (C, small square brackets) is inhibited in the vov; p53 double mutant (D). These surviving retinal cells do not laminate in the vov; p53 double mutant (D, large square bracket), suggesting that UPS is required for neuronal differentiation of retinal cells in a p53-independent manner. (E-H) EdU incorporation in wild-type (E), p53 (F), vov (G) and vov; p53 double mutant (H) lens at 72 hpf. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (red). EdU incorporation (green) does not occur in the retinal CMZ (small square bracket) and lens epithelium (large square bracket) in the vov mutant (G). In the vov; p53 double mutant, EdU incorporation is restored in the retinal CMZ, but the EdU-positive CMZ region is larger than in wild types and p53 mutants (H), suggesting that CMZ cells fail to exit from the cell cycle. EdU incorporation did not recover in the lens epithelium of the vov; p53 double mutant (H, large square bracket). (I-L) TUNEL staining (green) of wild-type (I), p53 (J), vov (K) and vov; p53 double mutant (L) lens at 72 hpf. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (red). TUNEL is detected in the neurogenic region near retinal CMZ in the vov mutant (K), whereas retinal apoptosis is suppressed in the vov; p53 double mutant (L). (M-P) Plastic sections of wild-type (M), p53 (N), vov (O) and vov; p53 double mutant (P) lens at 72 hpf. The vov; p53 double mutant shows defects in nuclear shape and position of lens fiber cells (P), which are similar to those of the vov mutant (O). (Q-T) Nuclear staining of wild-type (Q), p53 (R), vov (S) and vov; p53 double mutant (T) lens with DAPI at 72 hpf. (U) The number of lens fiber cell nuclei in the wild-type, vov, and vov; p53 double mutant at 72 hpf. The number of lens fiber cell nuclei in the vov; p53 double mutant is similar to that of wild type. (V) Ina of the vov; p53 double mutant is higher than that of wild type and similar to that of the vov mutant. The vov defects in nuclear position of lens fiber cells are not inhibited by the p53 mutation. (W) Inf of the wild type, vov, and vov; p53 double mutant. Like the vov mutant, the maximum Inf value of the vov; p53 double mutant is lower than that of the wild type, suggesting that the vov defects in nuclear shape of lens fiber cells are not inhibited by the p53 mutation. Student′s t-test (U,V,W). Scale bars: 50 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development