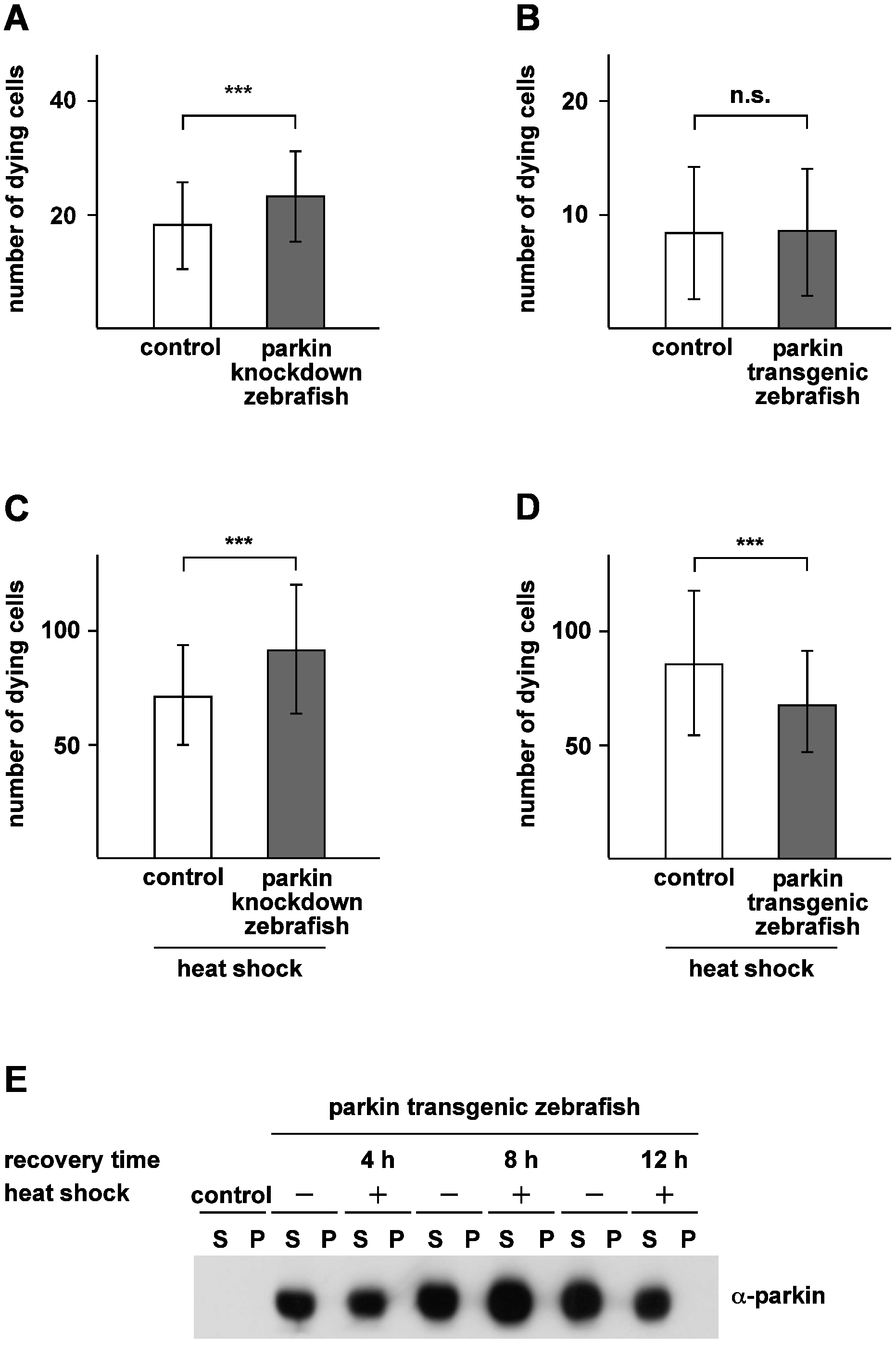
Fig. 11 Parkin protects zebrafish from heat shock-induced cell death.
(A) Basal cell death is slightly increased in parkin-deficient zebrafish. Two-day-old parkin knockdown zebrafish embryos and control-injected embryos were analyzed for dying cells in the spinal cord (neuronal and non-neuronal) by staining with acridine orange. Parkin-deficient zebrafish embryos showed a small but significant increase in basal cell death in comparison to control-injected embryos (23.20±7.96 versus 18.19±7.65 dying cells). (B) There is no difference in the rate of cell death between parkin transgenic zebrafish and non-transgenic littermates (8.37±5.82 versus 8.56±5.59 dying cells). (C+D) Parkin-deficient zebrafish are more vulnerable to thermal stress, while transgenic parkin zebrafish are more resistant to thermal stress. 48 hours post fertilization zebrafish embryos were exposed to a heat shock (39°C) for 1 h followed by an 8 h recovery period at 29°C. Staining with acridine orange was used to quantify dying cells (neuronal and non-neuronal) in the spinal cord. Cell death in response to thermal stress was increased in parkin knockdown zebrafish compared to control-injected fish (91.47±28,32 versus 71.0±21.96 dying cells) (C) and decreased in transgenic parkin zebrafish versus non-transgenic siblings (85.51±31.81 versus 67.39±22.26 dying cells) (D). Quantification was based on 3 independent experiments. For each experiment at least 50 embryos per group were analyzed. ***p<0.001. (E) Thermal stress in zebrafish had no effect on the detergent solubility of parkin. Western blot analysis of two-day-old transgenic parkin zebrafish embryos which were either heat shocked with subsequent recovery periods of 4 h, 8 h and 12 h, respectively, or remained untreated. After lysis of zebrafish embryos in detergent buffer, proteins were fractionated by centrifugation into detergent-soluble (S) and -insoluble (P) fractions, and parkin was analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-parkin antibody PRK8. Control: non-transgenic zebrafish embryos.