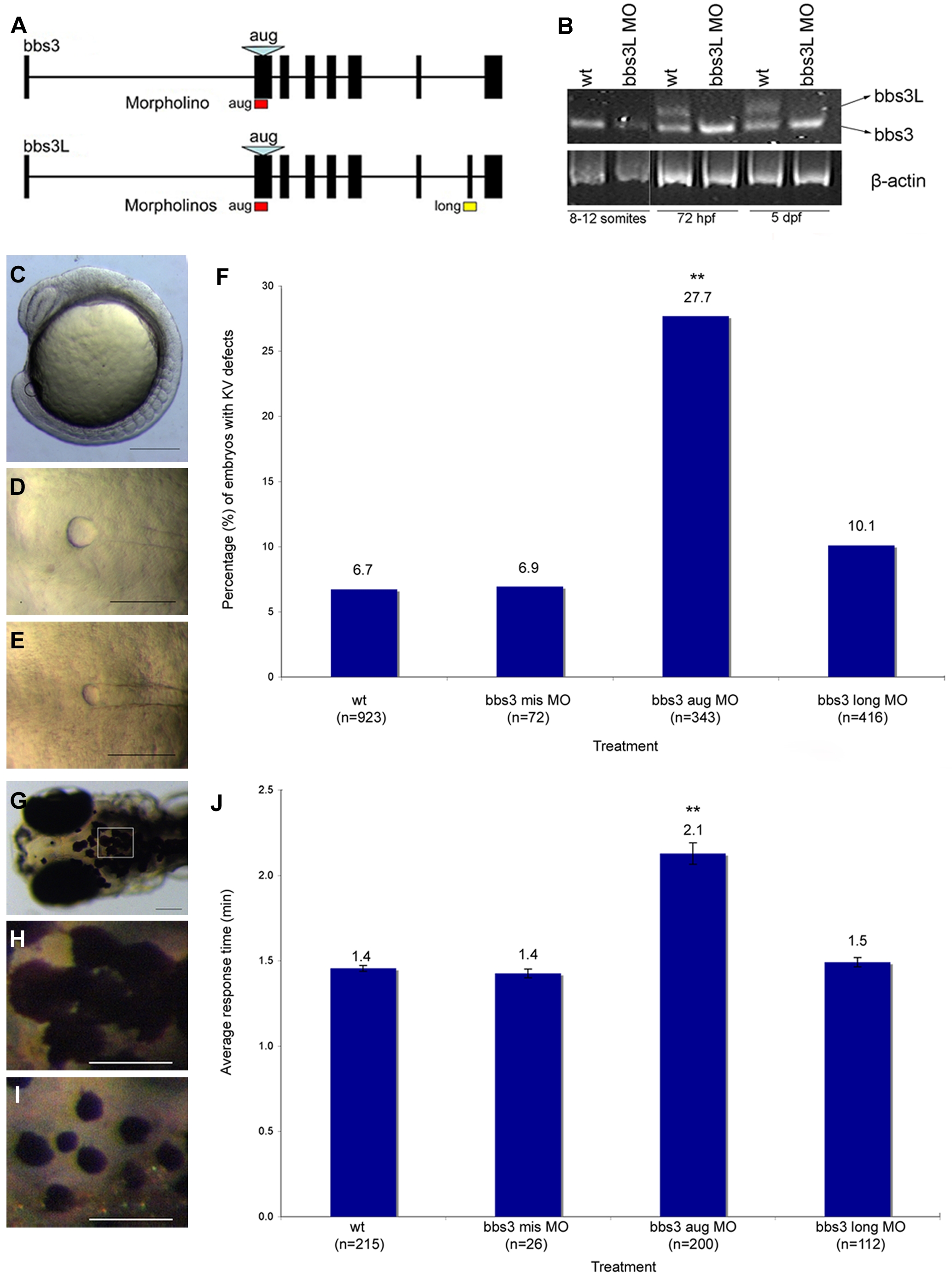
Fig. 2 bbs3 gene structure and cardinal features of BBS knockdown in zebrafish.
(A) Schematic depicting the bbs3 gene structure and antisense oligonucleotide strategy used to target either both transcripts (bbs3 aug MO) or to target only bbs3L (bbs3 long MO) in zebrafish embryos. The bbs3 aug MO targets the start site of the gene and thus hits both transcripts, while the bbs3L MO is a splice-blocking morpholino that only targets the long form. (B) RT-PCR from staged bbs3L morphant embryos at 8?12 somites, 72 hpf, and 5 dpf. The bbs3L transcript is absent through 5 dpf injected embryos indicating successful knockdown. Note that the bbs3 transcript is unperturbed in bbs3L morphants. (C?E) Images of live zebrafish embryos at 8?10 somite stage. Scale bar 200 μm. (C) Side view of an embryo highlighting the location of the Kupffer′s Vesicle (circle), the ciliated structure located in the tailbud. (D) Dorsal view of a normal sized KV from a wild-type embryo. (E) bbs3 aug MO?injected embryos with a reduced KV. (F) The percentage of embryos with KV defects (reduced or absent) in uninjected, control MO, bbs3 aug MO and bbs3 long MO injected embryos. The sample size (n) is noted on the x-axis. **Fisher′s Exact test, p<0.001. (G?I) Epinephrine-induced melanosome transport of wild-type 6-day old larvae. Scale bar 100 μm. (G) Melanosome transport is observed in cells on the head of the embryos. Boxed region is magnified for (H,I). (H) Wild-type larvae prior to epinephrine treatment and (I) the endpoint at 1.4 minutes after epinephrine treatment. (J) Epinephrine-induced retrograde transport times. The sample size (n) is noted on the x-axis. **ANOVA with Tukey, p<0.01.