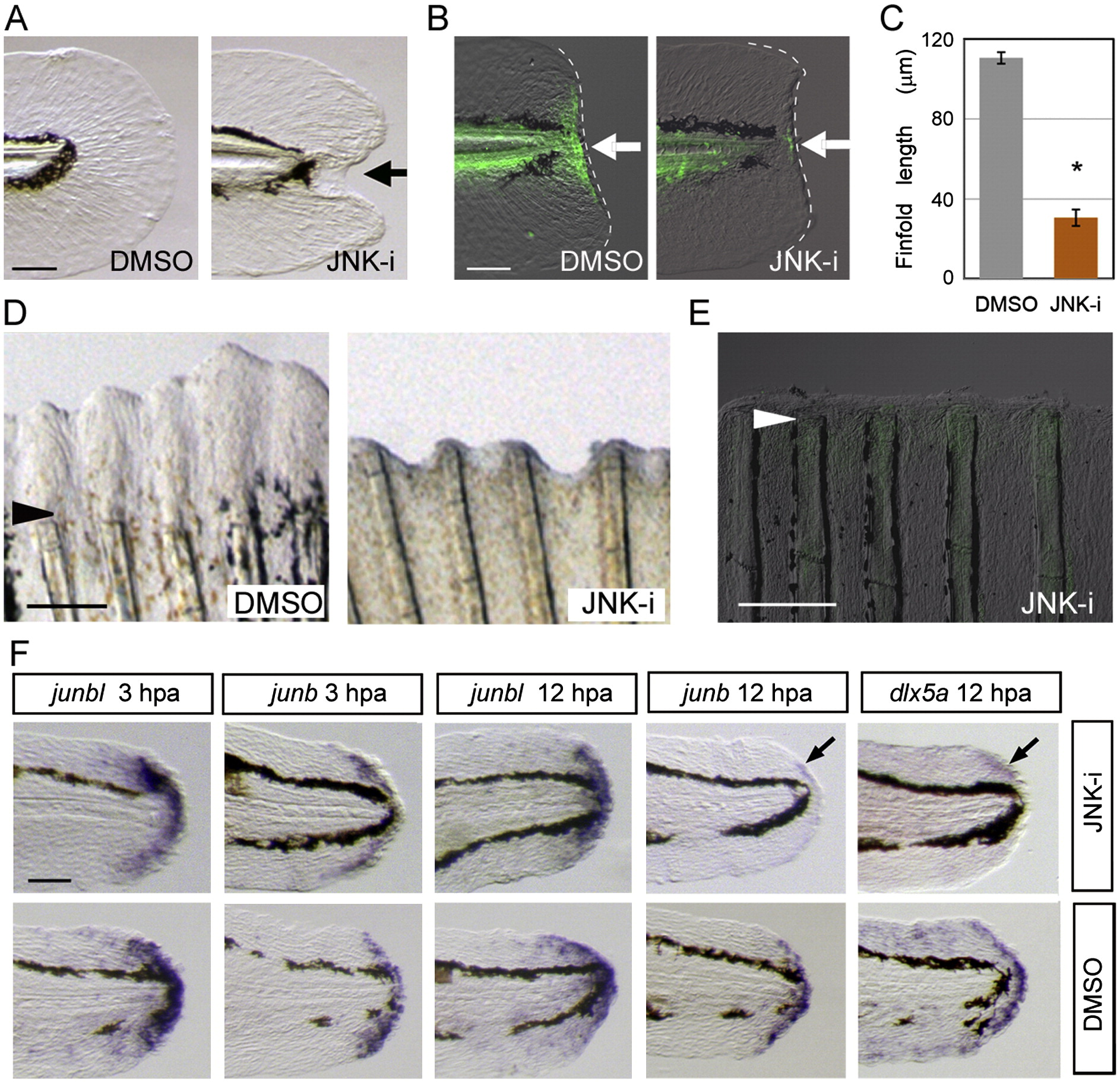
Fig. 3 Necessary roles of Jun protein phosphorylation by JNK for regeneration. (A) Impairment of finfold regeneration by inhibiting JNK signaling with SP600125 (5 μM), but not by the vehicle, DMSO (0.05%). (B) Down-regulation of Jun phosphorylation by the JNK inhibitor at 12 hpa. Arrows indicate the regeneration-dependent anti-pJun staining (left panel) and suppression by the inhibitor treatment (right panel). (C) Quantification of finfold regeneration. Regeneration was evaluated by the finfold length posterior to the notochord. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was tested by using Student′s t-test. *P < 0.001. (D) Suppression of adult fin regeneration by the JNK inhibitor at 4 dpa. (E) Down-regulation of Jun phosphorylation by the JNK inhibitor in adult fin regeneration at 2 dpa. Arrowheads in (D) and (E) indicate the site of amputation. (F) Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis for the expression of the blastema marker, junbl, and the wound epithelium markers, junb, and dlx5a at 3 hpa and 12 hpa in the presence (upper panels) or absence (lower panels) of the JNK inhibitor (10 μM). The gene expression was unaltered by the JNK inhibitor during the early stage. However, the later expression of epithelial genes, junb and dlx5a, at 12 hpa was down-regulated (arrows; n = 12 and 10, respectively) in spite of the maintained expression of junbl in the blastema. Respective gene expressions were confirmed by using more than 10 larvae for each probe. The scale bar represents 50 μm in (A), (B) and (F), and 100 μm in (D) and (E).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 340(2), Ishida, T., Nakajima, T., Kudo, A., and Kawakami, A., Phosphorylation of Junb family proteins by the Jun N-terminal kinase supports tissue regeneration in zebrafish, 468-479, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.