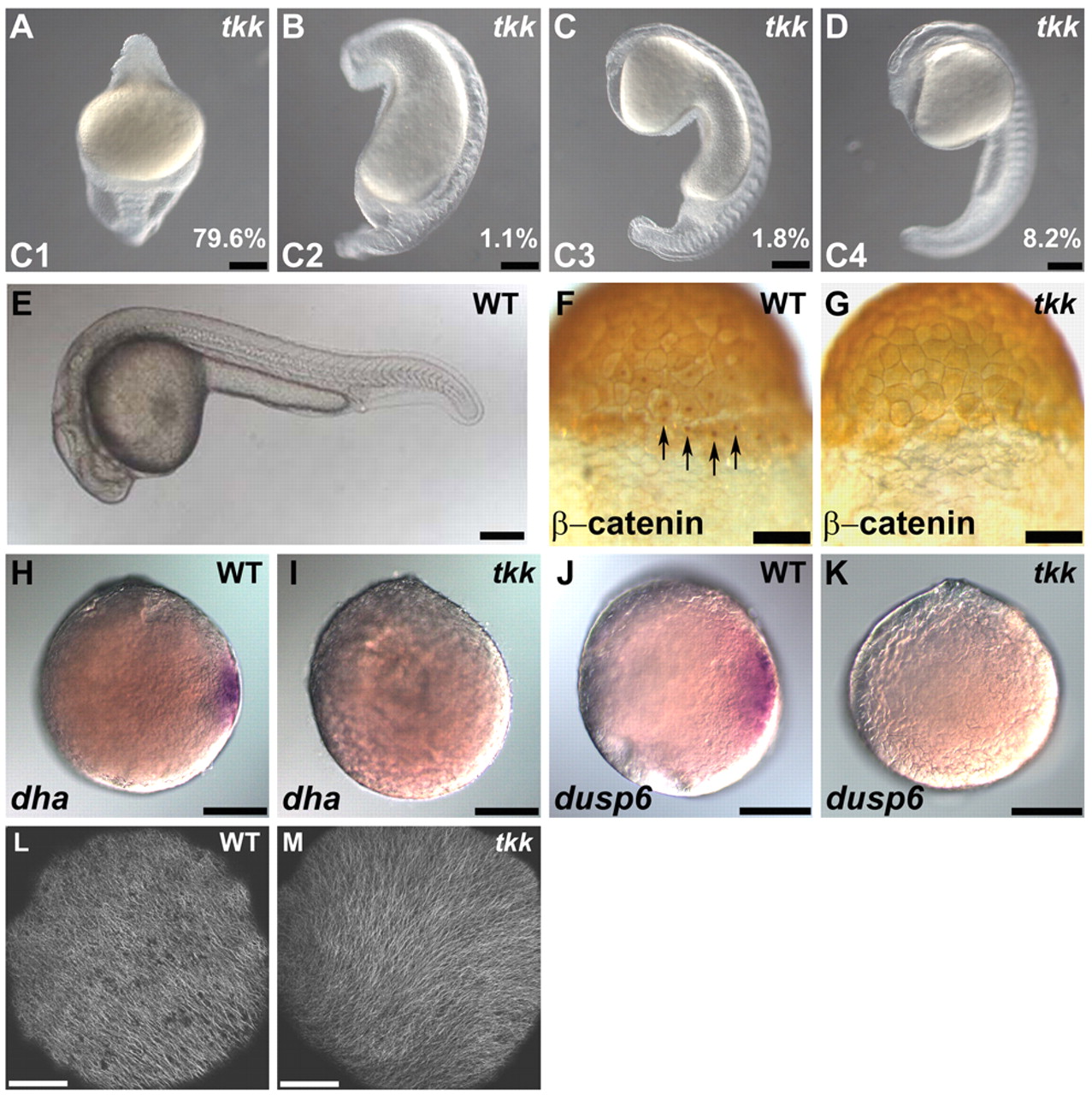
Fig. 1 Maternal-effect tokkaebi (tkk) mutant zebrafish embryos show defects in dorsal determination. (A-E) Phenotypes of tkk embryos (A-D) versus wild type (WT; E) at 24 hpf. Lateral views with dorsal to the right (A-D) or to the top (E). Embryos were classified into four classes (C1-4) based on their ventralized phenotypes. C1 embryos displayed a completely ventralized phenotype. C2 embryos were similar to C1 embryos but had somites in the trunk region. C3 embryos had somites and spinal cord in the trunk. C4 embryos had somites, spinal cord and hindbrain, but lacked notochord or neuroectoderm anterior to the midbrain. The percentage of tkk embryos from typical young females that showed each phenotype is indicated. (F,G) Immunostaining of β-catenin at the 256-cell stage in wild-type (F; 88%, n=26) and tkk (G; 11%, n=35) embryos. Dorsal views. Arrows indicate nuclear accumulation of β-catenin in dorsal blastomeres. (H,I) Expression of dha at sphere stage (4 hpf) in wild-type (H; 100%, n=36) and tkk (I; 8%, n=40) embryos. (J,K) Expression of dusp6 at sphere stage in wild-type (J; 100%, n=29) and tkk (K; 6%, n=36) embryos. Animal pole views. (L,M) Immunostaining with anti-β-tubulin antibody. Wild-type (L; 86%, n=14) and tkk (M; 81%, n=16) embryos at 20 mpf. Vegetal pole views. Scale bars: 200 μm in A-E,H-K; 140 μm in F,G; 20 μm in L,M.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development